Purification of organic compounds means separation of a particular organic compounds from impurities which are undesirable for us. When we obtain a chemical substance either from nature or by synthesis, they are not pure. Hence it is essential to purify them. We have included all the possible types of purification in this Purification of Organic Compounds: Short and Easy Notes. this notes has been written in simple manner and easy language so that any reader can easily take up this topic. Let’s start this notes.
Purification of organic substances is essential because sometimes we need pure organic compounds. Impure substances show variations in their qualities and properties. Here we shall learn all the important methods to separate impurities from any organic compounds.
Purification of Organic Compounds
There are five important methods for the purification of organic compounds .They are followings:
- Sublimation
- Crystallisation
- Distillation
- Differential extraction
- Chromatography
Principles and Techniques for purification
Now we shall learn the principles which will help us to decide that which method will be suitable to purify an organic compound. After that we shall use proper techniques to get pure organic compounds. At the last we shall also learn that how we can justify that obtained organic substances are pure or not. Let’s read the methods used for purification.
Purification of Organic Compounds by Sublimation
When a chemical substance converts directly into vapour phase from solid state on heating, this process is called sublimation.
This process is used for purification when either organic compound or impurities are volatile. In this process, impure substance is taken in a china dish covered with a perforated filter paper over which an inverted funnel is placed. On heating, vapours of the volatile solid rise up, pass through the holes in the filter paper and condense on the cooler walls of the funnel leaving behind the non volatile impurities in the dish.
For example camphor, benzoic acid, naphthalene etc.
Purification of Organic Compounds by Crystallisation
Crystals are the purest form of a substance having definite geometry. The process by which an impure compound is converted into its crystal is called crystallisation.
This is one of the most common method for the purification of solid organic compounds. This method is based on the principle that impurities and compounds should dissolve differently in a suitable solvent.
In this method, the impure compound is dissolved in a solvent in which it is sparingly soluble at room temperature but fairly soluble at higher temperature. Now the solution is concentrated to get a nearly saturated solution. On cooling the solution, pure compound is crystallises out and removed by crystallisation. For example benzoic acid, sugar.
Purification of Organic Compounds by Distillation
This method is used to separate volatile liquids from non volatile impurities and the liquids having sufficient difference in their boiling points. In this method, liquids having different boiling points vaporise at different temperatures. The vapours are cooled and the liquids so formed are collected separately. For example Chloroform (b.p. 334K) and aniline (b.p. 457K) are separated by this method.
Fractional distillation. If the difference in boiling points of two liquids is not much. The technique of fractional distillation is used in such cases for separation. In this method, vapours of liquid mixture are passed through a fractionating column before condensation. This method is used to separate different fractions of crude oil in petroleum industry.
Distillation under reduced pressure
This method is used to purify liquids having very high boiling points and decompose at or below their boiling points. In this method, such liquids are made to boil at a temperature lower than their normal boiling points by reducing the pressure on their surface. The pressure is reduced with the help of a water pump or vacuum pump. Glycerol can be separated from spent- lye in soap industry by this method.
Purification of Organic Compounds by Differential extraction
This method is used to separate an organic compound which is less soluble in water and more soluble in an organic solvent.
In this method, an organic compound in aqueous solution is separated by shaking with an organic solvent in which it is more soluble. The organic solvent and the aqueous solution should be immiscible with each other so that they form two distinct layers which can be separated by separatory funnel. The organic compound is later removed by distillation or evaporation to get back the compound.
For example benzoic acid can be extracted from its water solution using benzene as organic solvent.
Purification of Organic Compounds by Chromatography
It is the best way to separate mixtures into their compounds, purify compounds and to test the purity of compounds. In this method, the mixture of substances is applied onto a stationary phase, which may be a solid or liquid. A pure solvent, a mixture of solvents or a gas is allowed to move slowly over the stationary phase. The components of the mixture get gradually separated from one another. This moving phase is called the mobile phase.
Based on the principle involved, chromatography has been classified into many categories, but two of them are important for ncert syllabus. They are followings:
1. Adsorption chromatography
2. Partition chromatography
Adsorption chromatography . This method is based on the principle that different compounds are absorbed on an absorbent to different degrees. Commonly used adsorbents are silica gel and alumina. When a mobile phase is allowed to move over a stationary phase. The components of the mixture move by varying distances over the stationary phase.
Further, there are two types of partition chromatography as-
1. Column chromatography
2. Thin layer chromatography
Column Chromatography: ln this method, a mixture is separated by using a glass column that is filled with silica gel or alumina. The component with the highest affinity for the fixed phase is absorbed on the top of the column. A suitable eluent is allowed to flow down the column slowly. Depending on the degree to which the compounds are absorbed, complete separation takes place. The most readily adsorbed substances are retained near the top and others come down to various distances in the column. Finally, component is obtained by evaporation.
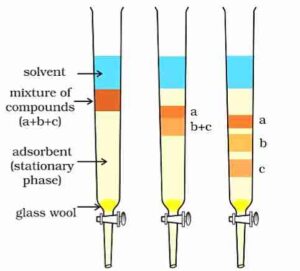
Thin Layer Chromatography:
In this chromatography, a sheet of alumina or silica gel as adsorbent (about 0.2 mm thick) spread over a glass plate of suitable size. The solution of the mixture is put as a small spot about 2 cm above one end of the TLC plate. The spots of coloured compounds are visible on TLC plate. Sometimes A suitable reagent may be also sprayed on the plate for visibility. For example amino acid may be detected by spraying the plate with ninhydrin solution.
Partition Chromatography. This method is also known as paper chromatography. In this method, a strip of chromatography paper spotted at the base with the solution of the mixture is suspended in a suitable solvent. This solvent rises up the paper by capillary action and flows over the spot. The paper selectively retains different components according to their differing partition in two phases.
The spots of the separated coloured compounds are visible at different heights from the position of initial spots. The spots of the separated colourless compounds may be observed under ultraviolet light.
Purification of Organic Compounds by Filtration
This is a simple method for the purification of organic compounds. In this method insoluble sold is separated from soluble substance by dissolving in a solvent. For example naphthalene and urea can be separated by this method. Urea is soluble in water but naphthalene is insoluble. They are dissolved in water and after filtration, urea left in solution but naphthalene stays on the filter paper.
Summary
We hope that you must have read
Purification of Organic Compounds Short and Easy Notes completely. All the important methods for purification of organic compounds have been included in this notes. They are distillation, crystallisation, sublimation, differential extraction and chromatography. The simple method of purification is Filtration has been also discussed in this notes. The best method of purification is chromatography. All the types of chromatography have been explained in proper and easy way.
We expect that this notes has been beneficial and feel good. Then we shall request you to share the link of this notes among your friends and favourites. Thanks for reading this notes.
FAQ in Purification of Organic Compounds
Q.No 1. What is the easiest purification method?
Ans:- Filtration is the easiest purification method.
Q.No 2. What are the 5 steps of purification?
Ans:- Filtration, sublimation, distillation, crystallisation and chromatography are the best ways for purification.
Q.No 3. What means ‘eluent’ in column chromatography?
Ans:- In column chromatography, a suitable solvent is used to extract different compounds adsorbed on the column is known as eluent.
Q.No 4. How will you purify an organic liquid which decomposes below its boiling point?
Ans:- Distillation under reduced pressure or vacuum distillation.
Q.No 5. Which chemical is used to purify?
Ans:- All the compounds either isolated from natural sources or by synthesis are used to purify. This is because to characterise it perfectly.

