Ncert Solutions of Chemical Kinetics is important for us in many ways. This is the 3rd chapter of chemistry for class 12th according to the revised syllabus of Ncert patterns. Here, all the questions of intext and exercise have been uploaded with solution in easy and simple manner. Any student can learn and understand to solve these questions. By going through these solutions, they can score good marks in any exams. Therefore, you all are suggested to read continue till end.
Chemical kinetics is the most interesting chapter of physical chemistry. In this chapter we learn about the speed or the rate of chemical reactions, mechanism of the reactions process and the factors which affect the rate of reactions. During study of this chapter we shall learn about order of reaction, molecularity, Arrhenius equation, collisions theory and so more.
Ncert Solutions of Chemical Kinetics will also help to derive a number of formulas and techniques to solve numerical problems. These solutions will enhance your grip on the basic concepts of this chapter. After reading this solution notes, you can deserve to score good marks in entrance and competitive exams like Jee(mains), Neet, IIT advance and some other board exams. Hence, again you are requested to remain till the end in this article.
Objectives of Ncert Solutions of Chemical Kinetics
- To define the average and spontaneous rate of a reaction.
- To express the rate of reaction in terms of change in concentration of either of the reactants or products with time.
- To distinguish between elementary and complex reactions.
- To differentiate between the order of reaction and molecularity.
- To define rate constant.
- To discuss the dependence of rate of reactions on concentration, temperature and catalyst.
- To derive integrated rate equations for zero and first order reactions.
- To determine the rate constants for the zero and first order reactions.
- To describe collision theory.
Read More: Chemical Kinetics Class 12: Notes For Chapter 4 Chemical kinetics
Answers of Intext questions in Ncert Solutions of Chemical Kinetics
Question 1. For the reaction R → P, the concentration of reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
Answer: 
Question 2. In a reaction, 2A → Products, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5 mol L-1 to 0.4 molL-1 in 10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this interval?
Answer: 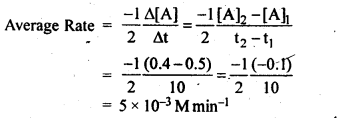
Question 3. For a reaction, A + B → Products, the rate law is given by : r = k [A]1/2[B]2. What is the order of reaction?
Answer: Rate law (r ) = k [A]1/2[B]2. ∴ Order of reaction = 1/2 + 2 = 5/2 = 2.5
Question 4. The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y ?
Answer: The conversion of molecules X → Y follows second order kinetics. The rate law equation will be: r = k [X]2 = ka2 (If [X] = a mol L-1). If concentration of X is increased three times, now, [X] = 3a mol L-1 ∴ Rate = k (3a)2 = 9ka2. Thus the rate of reaction will become 9 times and the rate of formation of Y will increase 9 times.
Question 5. A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 x 10-3 s-1. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g?
Answer: 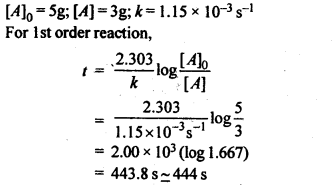
Question 6.Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Answer: For a first order of reaction, K = 0.693 / t1/2 = 0.693 / 60 min = 1.155 × 10–2 min–1 or 0.693 / 60 × 60 s = 1.925 × 10–4 s–1.
Question 7. What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
Answer: The rate constant of a reaction is nearly doubled with rise in temperature by 10oC. The exact effect of temperature on rate constant is given by Arrhenius equation, K = Ae–Ea/RT where A is called frequency factor and Ea is the activation energy of the reaction.
Question 8. The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for and increase of 10 K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
Answer: 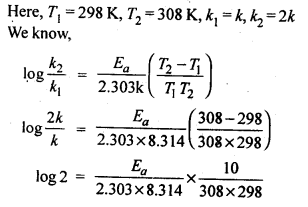
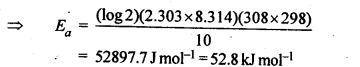
Question 9. The activation energy for the reaction, 2 HI(g) → H2+I2 (g) is 209.5 k J mol-1 at 581 K.Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
Answer: As it is known that fraction of molecules having energy equal to or greater than activation energy. Hence, 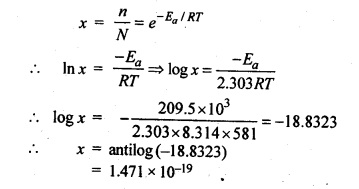
Answers of Exercise questions in Ncert Solutions of Chemical Kinetics
Question 1. From the rate expression for the following reactions determine their order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constants: 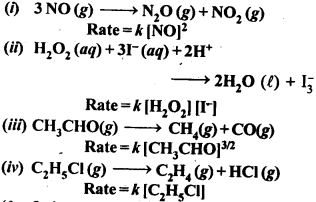
Answer: 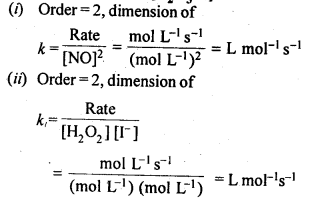
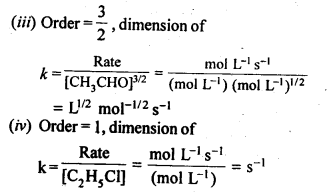
Question 2. For the reaction ; 2A + B → A2B, the reaction rate = k [A][B]2 with k = 2·0 x 10-6 mol-2 L2 s-1. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0·1 mol L-1; [B] = 0·2 mol L-1. Also calculate the reaction rate when [A] is reduced to 0·06 mol L-1.
Answer: Initial rate = K [A] [B]2 = (2.0 × 10–6) × (0.1) × (0.2)2 = 8 × 10–9 mol L-1 s–1. According to the reaction, when [A] is reduced from 0.1mol L-1 to 0·06 mol L-1. That means 0.04 mol L-1 of A has reacted, then B reacted = 1/2 × 0.04 = 0.02 mol L-1 Hence left [B] = 0.2 – 0.02 = 0.18 mol L-1 Now, rate = (2·0 x 10-6 mol-2 L2 s-1) × (0·06 mol L-1) × (0.18 mol L-1 )2 = 3.89 × 10–9 mol L-1 s–1.
Question 3. The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of N2 and H2 if Ar = 2.5 x 10-4 mol-1 Ls-1.
Answer: 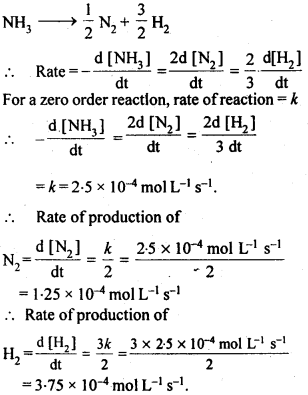
Question 4. The decomposition of dimethyl ether leads to the formation of CH4, H2 and CO and die reaction, rate is given by Rate=k [CH3OCH3]3/2 The rate of reaction is followed by increase in pressure in a closed vessel, so the rate can also, be expressed in terms of the partial pressure of dimethyl ether, i.e., Rate = k (PCH3OCH3)3/2
If the pressure is measured in bar and time in minutes, then what are the units of rate and rate constants?
Answer: When concentration terms are taken in terms of pressure, 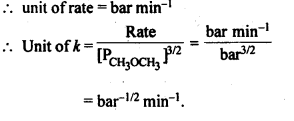
Question 5. Mention the factors that effect the rate of chemical reaction.
Answer: The rate of any particular reaction depends upon the following factors:
- Nature of the reactants: Different amounts of energies are required for breaking of different bonds.
- Concentration: Greater are the concentration of reactants, faster is the reaction.
- Temperature: The rate of reaction increases with increase in temperature. In most of the cases, the rate of reaction becomes nearly double for 10o rise in temperature.
- Presence of catalyst: A catalyst generally increases the speed of a reaction without consuming itself.
- Surface area of the reactants: Greater is the surface area, faster is the reaction.
- Presence of light: Some reactions do not take place in the dark but take place in the presence of light. Ex. Photochemical reactions.
Question 6. A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is (i) doubled (ii) reduced to 1/2 ?
Answer: Rate = K [A]2 = Ka2. If [A] = 2a, rate = K (2a)2 = 4 Ka2 that means rate of reaction becomes 4 times. If [A] = 1/2a, rate = K (1/2a)2 = 1/4 Ka2 that means rate of reaction becomes 1/ 4 times.
Question 7. What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reaction? How can this temperature effect on the rate constant be represented quantitatively?
Answer: The rate constant of a reaction increases with increase of temperature and becomes nearly double for every 10o rise of temperature. The effect can be represented quantitatively by Arrhenius equation as k = A.e –Ea/RT where Ea is the activation energy of the reaction and A represents the frequency factor.
Question 8. In a pseudo first order hydrolysis of an ester in water, the following results are obtained:
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 |
| [Ester]/mol L–1 | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.085 |
(i) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds. (ii) Calculate the pseudo first order rate constant for the hydrolysis of ester.
Answer: 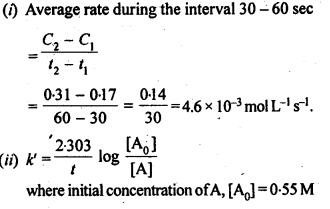
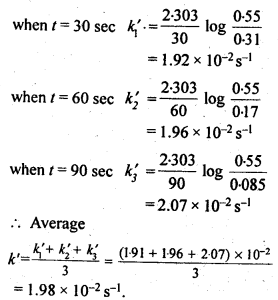
Question 9. A reaction is first order in A and second order in B.
(i) Write the differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B is doubled?
Answer: 
Question 10. In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below: 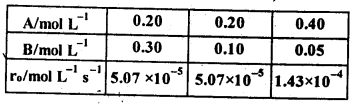
What is the order of reaction with respect to A and B ?
Answer: 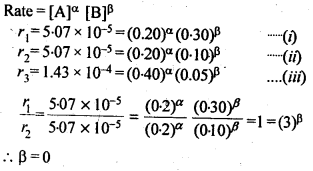

Question 11. The following results have been obtained during the kinetic studies of the reaction.
2A+B → C + D 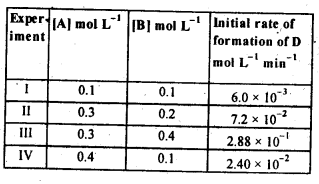
What is the rate law ? What is the order with respect to each reactant and the overall order ? Also calculate the rate constant and write its unit.
Answer: 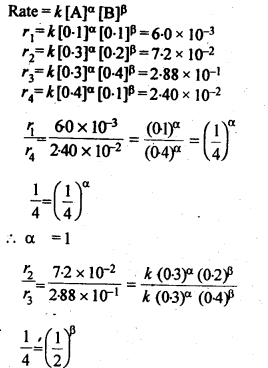
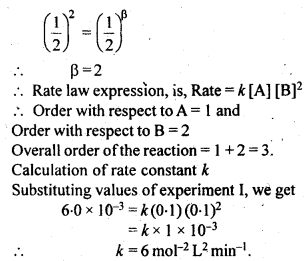
Question 12. The reaction between A and B is first order with respect to A and zero order with respect to B. Fill in the blanks in the following table: 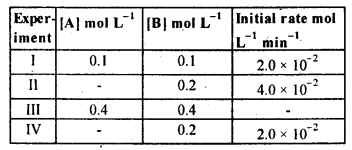
Answer: The rate expression will be: Rate = K [A]1[B]0 = k[A]. For expat. I, 2.0 × 10–2 mol L-1 min–1 = k (0.1 mol L-1) or K = 0.2 min–1. For expt. II, 4.0 × 10–2 mol L-1 min–1 = 0.2 min–1 × [A] or [A] = 0.2 mol L-1. For expt. III, Rate = ( 0.2 min–1) × (0.4mol L-1) = 0.08 mol L-1 min–1. For expt. IV, 2.0 × 10–2 mol L-1 min–1 = 0.2 min–1 × [A] or [A] = 0.1 mol L-1.
Question 13. Calculate the half life of a first order reaction from their rate constants given below: (a) 200 s–1 (b) 2 min–1 (c) 4 year–1
Answer: Half life period of a first order of reaction is given by: t1/2 = 0.693 / K. (a) t1/2 = 0.693 / 200 s–1 = 0.346 × 10–2 s = 3.46 × 10–3 s. (b) t1/2 = 0.693 / 2 min–1. = 0.346 min. (c) t1/2 = 0.693 / 4 year–1 = 0.173 years.
Question 14. The half life for radioactive decay of 14C is 5730 years. An archeological artifact contained wood that had only 80% of the 14C found in living tree. Estimate the age of the sample.
Answer: As we know that Radioactive decay follows first order kinetics hence 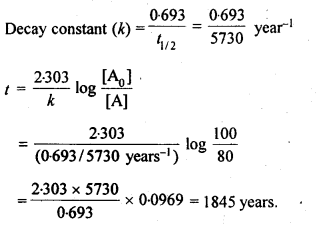
Question 15. The experimental data for decomposition of N2O5 
Answer : 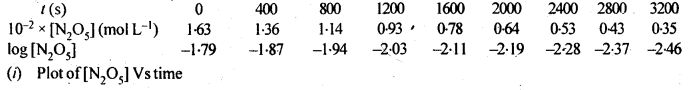
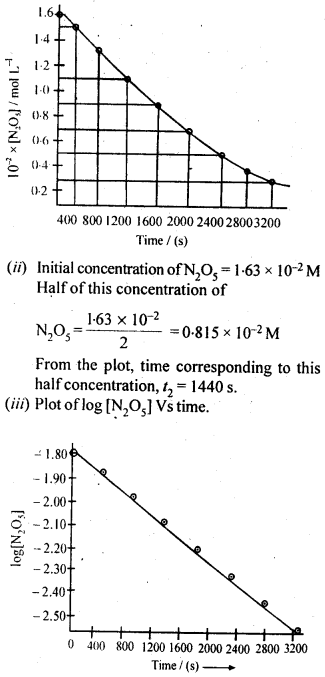
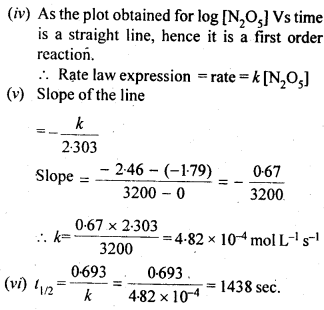
Question 16. The rate constant for a first order reaction is 60 s-1. How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration of the reactant to its 1/16 th value ?
Answer: 
Question 17. During nuclear explosion, one of the products is 90Sr with half-life of 28.1 years. If 1 µg of 90Sr was absorbed in the bones of a newly born baby instead of calcium, how much of it will remain after 10 years and 60 years if it is not lost metabolically ?
Answer: 
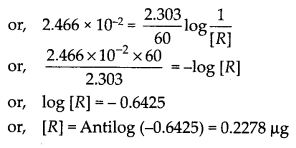
Question 18. Show that for a first order reaction the time required for 99% completion of a reaction is twice the time required to complete 90% of the reaction.
Answer: 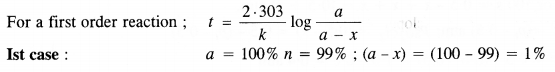
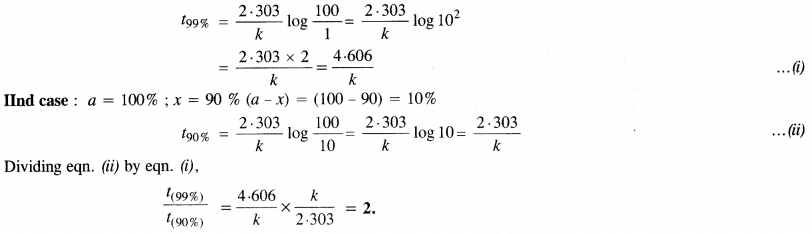
Question 19. A first order reaction takes 40 min for 30% decomposition. Calculate t1/2.
Answer: 
Question 20. For the decomposition of azoisopropane to hexane and nitrogen at 543 K. The following data are obtained: 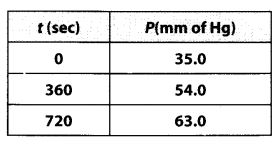
Calculate the rate constant.
Answer: 
Question 21. The following data were obtained during the first order under thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume: SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2(g).
| Experiment | Time/s | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6 |
Answer : 
Question 22. The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below: 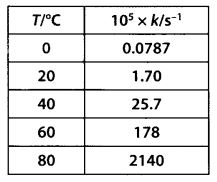
Draw a graph between ln K and 1/T and calculate the value of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30oC and 50oC.
Answer: The values of rate constants for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures are given below : 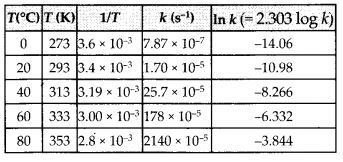
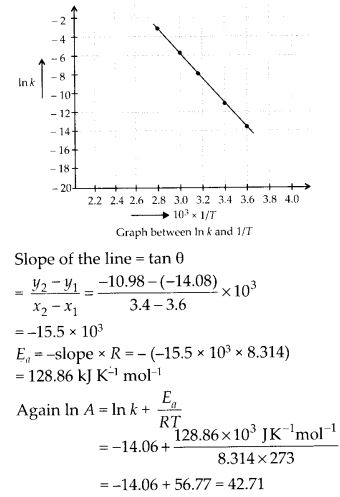

Question 23. The rate constant for the decomposition of a hydrocarbon is 2.418 × 10–5 s–1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 KJmol-1. What will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
Answer: Here, K= 2.418 × 10–5 s–1 , Ea = 179.9 KJmol-1 ,T= 546K. According toArrhenius equation: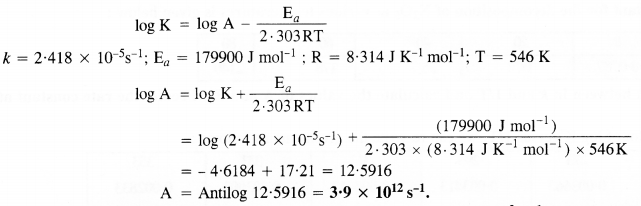
Question 24. Consider a certain reaction A → products with K = 2.0 × 10–2 s–1 . Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100 s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L-1.
Answer : 
Question 25. Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law with t1/2 = 3.00 hours. What fraction of the sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours?
Answer: As sucrose decomposes according to the first order rate law, 
Question 26. The decomposition of a hydrocarbon follows the equation K = (4.5 × 1011 s–1) e–2800 K / T. Calculate Ea.
Answer: According to 
Question 27. The rate constant for the first order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation: log K = 14.34 – 1.25 × 104 K / T. Calculate Ea for this reaction and at what temperature will its half period be 256 minutes?
Answer: 

Question 28. The decomposition of A into product has value of K as 4.5 × 103 s–1 at 10oC and energy of activation 60 KJmol-1. At what temperature would K be 1.5 × 104 s–1 ?
Answer: 
Question 29. The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298 K is equal to that required for its 25% completion at 308 K. If the value of A is 4 × 1010 s–1, calculate K at 318 K and Ea.
Answer: 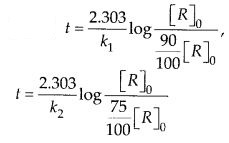


Question 30. The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
Answer: 

