Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons: This is the chapter which gives detail idea about Hydrocarbons. These are the basic or fundamental organic compounds. We shall learn various kinds of reactions which boost our knowledge in organic chemistry and will have a good hold on each and every topics of organic chemistry. We shall have our best try to solve all the questions given in the exercise of Ncert book of chemistry. Let’s read out this solution paper till end.
Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons is the ninth chapter according to the revised syllabus of Ncert organic chemistry for class 11th. In this chapter, we have to read about Hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are those compounds which consist only hydrogen and carbon. For example Methane, ethylene, acetylene, benzene. We have to read about the kinds of hydrocarbons, their preparations and properties. Besides them, we have to learn many things about these compounds.
Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons: Objectives
- To name hydrocarbons according to IUPAC system.
- To recognize and write structures of isomers of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons.
- To learn about various methods of preparation of hydrocarbons.
- To distinguish between alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons on the basis of physical and chemical properties.
- To draw and differentiate between various conformations of ethane.
- To appreciate the role of hydrocarbons as source of energy and for other industrial applications.
- To predict the formation of the addition products of unsymmetrical alkenes and alkynes in the basis of electronic mechanisms.
- To compare the structure of benzene, explain aromaticity and understand mechanism of electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene.
- To predict the directive influence of substituents in monosubstituted benzene ring.
- To learn about carcinogenicity and toxicity.
Solution of Questions in Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons:
Question 1. How do you account for formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: Chlorination of methane is a free radical reaction which occurs by the following mechanism: 
From the above mechanism, it is clear that CH3 free radicals are formed during propagation step which undergo three reactions. In the chain termination step, the two CH3 free radicals combine together to form ethane and its formula is CH3-CH3.
Question 2. Write IUPAC name of the following compounds. 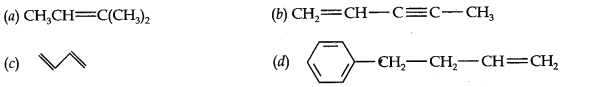

Answer: 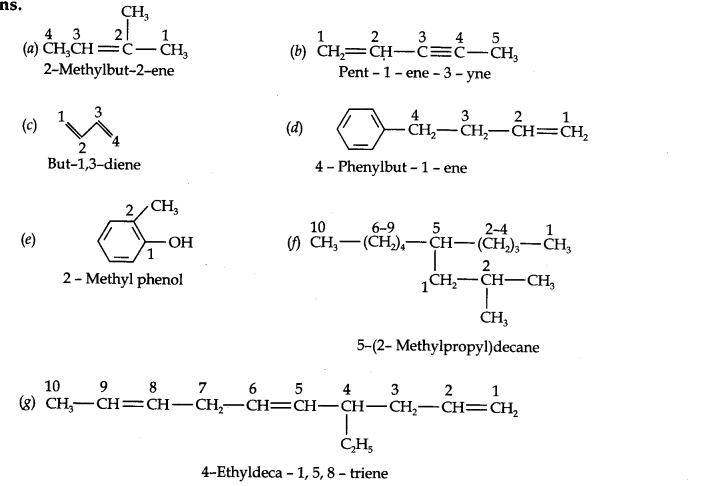
Question 3. For the following compounds, write structural formulas and IUPAC names for all possible isomers having the number of double or triple bond as indicated: (a) C4H8 (one double bond) (b) C5H8 (one triple bond)
Answer: (a) Isomers of C4H8 having one double bond are: 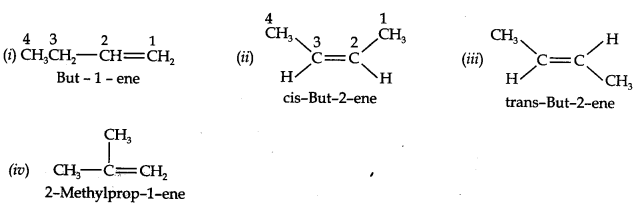
(b) Isomers of C5H8 having one triple bond are: 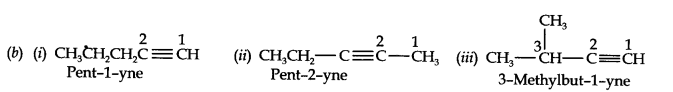
Question 4. Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds: (i) Pent-2-ene (ii) 3,4-Dimethylhept-3-ene (iii) 2-ethyl but-1-ene (iv) 1-phenylbut-1-ene. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: 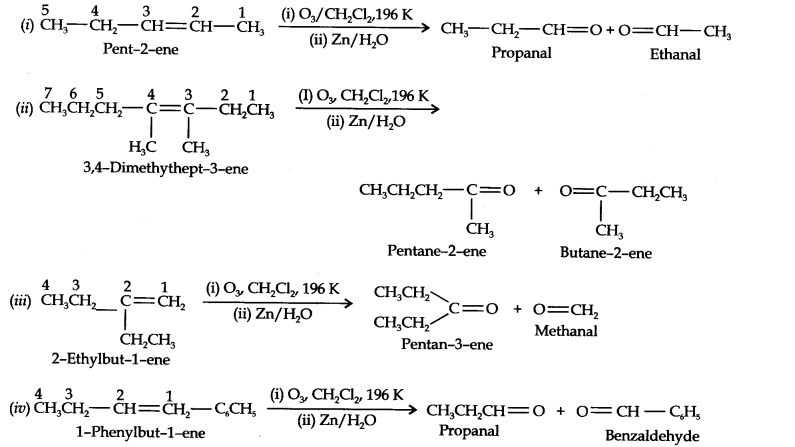
Question 5. An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanol and pent-3-one. Write the structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: In step 1. Write the structure of the products side by side with their oxygen atoms pointing towards each other. 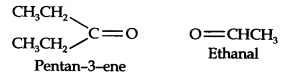
In step 2. Remove the oxygen atoms and join the two ends by a double bond, the structure of the alkene ‘A’ will be 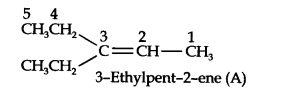
Question 6. An alkene ‘A’ contains three C–C, eight C–H, σ- bonds,and one C–C π- bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of aldehyde of molar mass 44u write the IUPAC name of ‘A’. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: An aldehyde of molar mass 44u is Ethanal and its formula is CH3CH=O. Now write two moles of Ethanal side by side with their oxygen atoms pointing towards each other as CH3CH=O + O=CHCH3. Further remove the oxygen atoms and join them by a double bond. At final we get the structure of ‘A’ as CH3–CH = CH–CH3 or 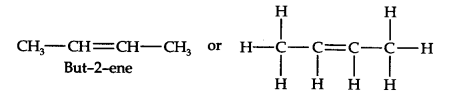
As per question, but-2-ene has three C–C, eight C–H ο-bonds and one C–C π-bond.
Question 7. Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis products of an alkene. What is the structural formula of the alkene? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: First upon all write the structures of propanal and pentan-3-one with their oxygen atoms pointing each other, we have, 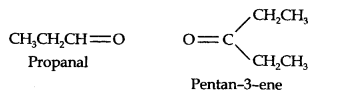
Now remove oxygen atoms and joins the both fragments by double bond the structure of the alkene is 
Question 8. Write chemical equations for the combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbons. (i) Butane (ii) Pentene (iii) Hexyne (iv) Toluene. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: 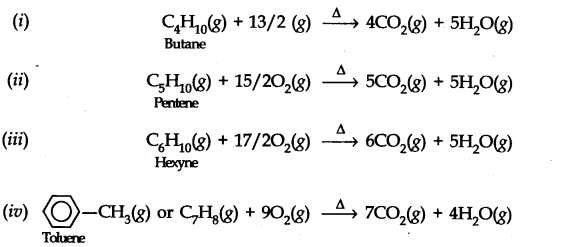
Question 9. Draw the cis- and trans- structures for hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher b.p. and why?
Answer: The structures of cis- and trans- isomers of hex-2-ene can be shown as: 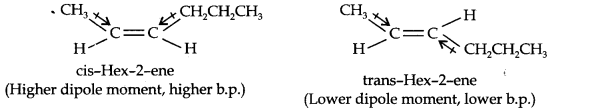
The boiling point of a molecule depends upon dipole dipole interactions. Since cis- isomer has higher dipole moment, therefore, it has higher boiling point.
Question 10. Why is benzene extra ordinary stable though it contains three double bonds? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: Resonance of electrons generally leads to the stability. Since in benzene all the six π-electrons of the three double bonds are completely delocalised to form one lowest energy molecular orbital which surrounds all the carbon atoms of the ring. Therefore it is extraordinary stable. Delocalisation of 6 π- electrons can be represented as: 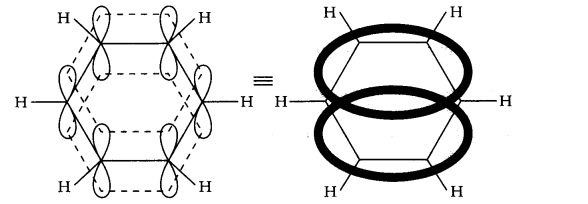
Question 11. What are the necessary conditions for any system to be aromatic? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: The necessary conditions for a molecule to be aromatic are followings:
- It should have a single cyclic cloud of delocalised π-electrons above and below the plane of the molecule.
- It should be planar.
- It should have huckle number of electrons, i.e., (4n + 2) π-electrons where n = 0, 1, 2, 3 ….. etc.
- A molecule which does not satisfy any one or more of the above conditions is said to be non- aromatic.
Question12. Explain why the following systems are not aromatic? 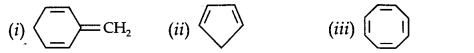
Answer: (i) In this compound, C4 is sp3 hybridised hence it is non- planar. It does contain six π- electrons but the system is not fully delocalised since all the six pi electrons do not form a single cyclic electron cloud which surrounds all the atoms of the ring that is why, it is not an aromatic compound.
(ii) In this compound, one carbon atom is sp3 hybridised and it contains only four π- electrons. It does not contain planar cyclic cloud having (4n + 2)π electrons. Therefore, it is not aromatic.
(iii) Cyclooctatetraene is not planar but it is tub shaped. It is non- planar system having 8 π-electrons. It does not contain a planar cyclic cloud having (4n + 2) π- electrons. Therefore, this molecule is not aromatic. 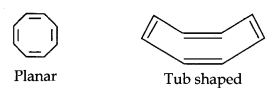
Question 13. How will you convert benzene into. (i) p- nitrobromobenzene (ii) m-nitrochlorobenze (iii) p-nitrotoluene (iv) acetophenone? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer : (i) For this conversion, Br atom should be introduced by Bromination in the benzene ring and this should be followed by nitraton according to the following reactions: 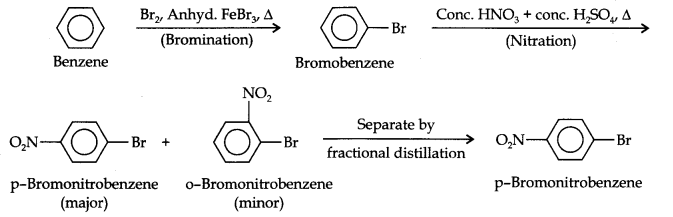
(ii) In this conversion, NO2 group should be introduced by nitraton and this should be followed by chlorination according to the following reactions: 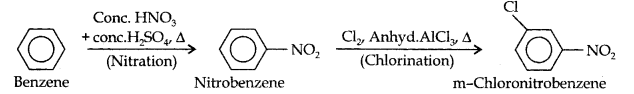
(iii) In this conversion, at first, CH3 group should be introduced by Friedel crafts reaction and this should be followed by nitraton. Finally p-nitrotoluene should be separated by fractional distillation. 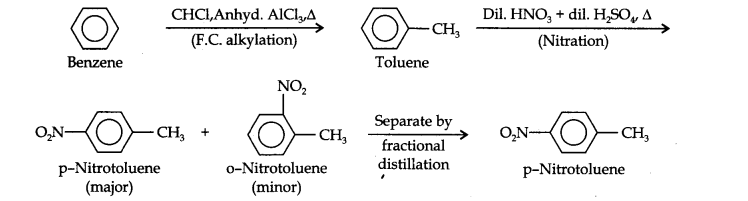
(iv) In this conversion, Acetophenone can be prepared by F.C.acylation using either acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride. 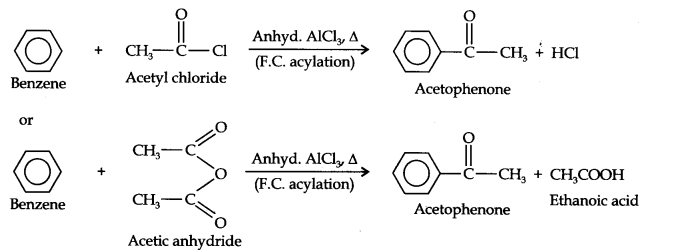
Questions 14. In the alkane, CH3CH2 – C (CH3)2 – CH2 – CH(CH3)2. Identify 1o, 2o, 3o carbon atoms and give the number of H-atoms bonded to each one of these. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: The expanded structural formula of the given compound is 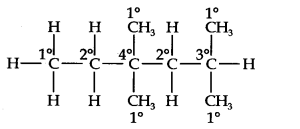
1oC = 5 and attached H-atoms = 15, 2oC = 2 and attached H-atoms = 4, 3oC = 1 and attached H-atoms = 1
Question 15. What effect does branching of an alkene chain has on its boiling point? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: As the branching in an alkene increases, its surface area decreases results in vander waals forces of attraction decreases and hence, the boiling point of the alkene decreases.
Question 16. Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while in presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism.
Answer: Addition of HBr to propane is an electrophilic addition reaction in which the electrophile H+ first adds to give a more stable 2o carbocation. In the 2nd step, the carbocation is quickly attacked by the nucleophile Br– to give 2-bromo propane. 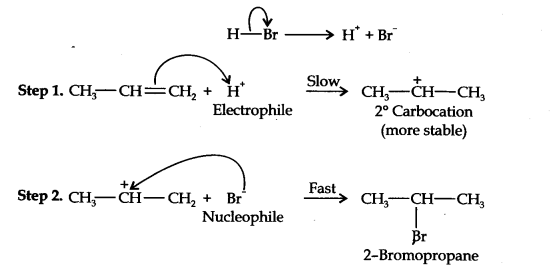
In presence of benzoyl peroxide, the reaction proceeds with free radical addition reaction. Here, Br• is a free radical which is obtained by the action of benzoyl peroxide on HBr. 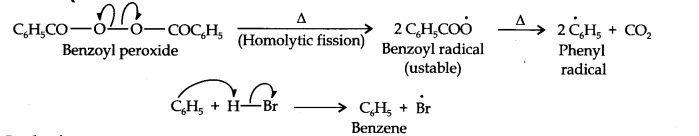
Now, in the first step, bromine radical adds to propene in such a way so as to generate the more stable 2o free radical carbocation. In the 2nd step, the free radical thus obtained rapidly abstract a hydrogen atom from HBr to give 1- bromo propane. 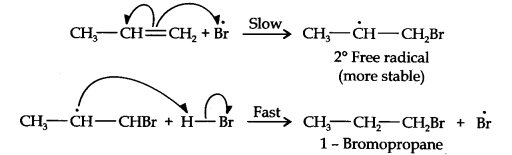
Question 17. Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result Support kekule structure of benzene? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: o-xylene may be regarded as a resonance hybrid of the following two kekule structure. Ozonolysis of each one of these gives two products as shown below: 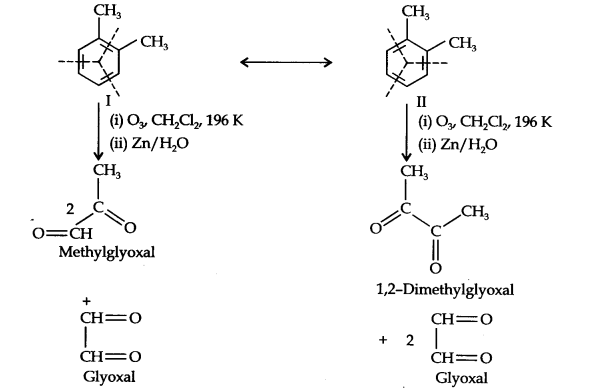
From the above results, it is clear that all the three products can not be obtained from any one of the two kekule structures. Hence, it can be justified that o-xylene is a resonance hybrid of the two kekule structures.
Question 18. Arrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in degreasing order of acidic behaviour.
Answer. Let’s have a look on the hybridisation state of carbon in these three compounds as: 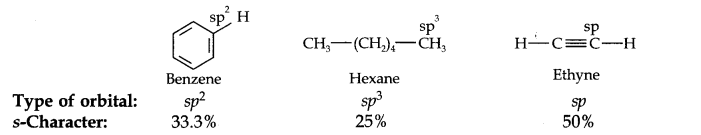
As s-electrons are closer to the nucleus, therefore, the electronegativity of the carbon atom increases and tendency to give H+ ions increases results in acidic character increases thus the order of acidic character will be: Ethyne > Benzene > n-hexane
Question 19. Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitution difficulty? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: Due to the presence of an electron cloud containing 6π-electrons above and below the plane of the ring, benzene is a rich source of electrons. As a result, it attracts the electrophilic reagents towards it and repels nucleophilic reagents. That is why, benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitution reactions with difficulty.
Question 20. How will you convert the following compounds into benzene? (¡) Ethyne (ii) Ethene (iii) Hexane. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: 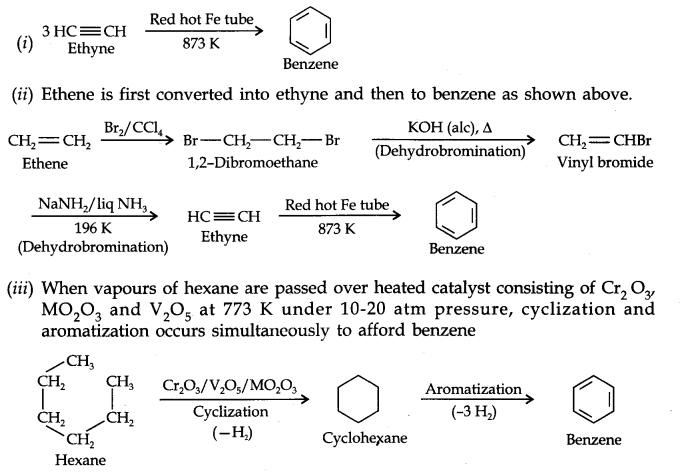
Question 21. Write the structure of all the alkenes which on hydrogenation give 2- methylbutane.
Answer: 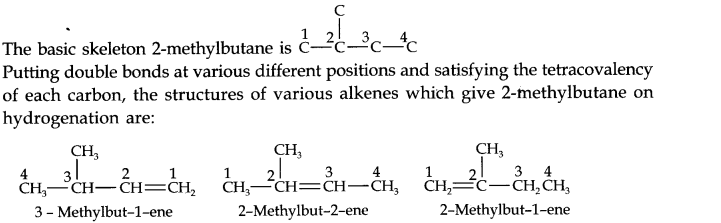
Question 22. Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+. (a) Chlorobenze, 2,4-di nitrochlorobenze, p-nitrochlorobenzene. (b) Toluene, p-H3C–C6H4—NO2, p-O2N– C6H4—NO2. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: (a)The typical reactions of benzene are electrophilic substitution reactions. Higher the electron density in the benzene ring, more reactive is the compound towards these reactions. Since, NO2 is a more powerful electron withdrawing group than Cl, therefore, more the number of nitro group, less reactive is the compound. Thus, the overall reactivity decrease in the order: Chlorobenze > p-chlorobenzene > 2,4-di nitrochlorobenzene.
(b) Here CH3 group is electron donating group but NO2 group is electron withdrawing. Therefore, the maximum electron density will be in toluene, followed by p-nitrotoluene and then by p-dinitrobenzene. Thus, the overall reactivity decreases in the order: Toluene > p-H3C–C6H4—NO2 > p-O2N– C6H4—NO2.
Question 23. Out of benzene, m-dinitro benzene and toluene which will undergo nitraton most easily and why? (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: CH3 group is electron donating while NO2 group is electron withdrawing. Therefore, maximum density will be in toluene, followed by benzene and least in m-dinitrobenzene. Therefore, the ease of nitraton decrease in the order: toluene > benzene > m-dinitrobenzene.
Question 24. Suggests the name of a Lewis acid other than anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: Ethylation means introduction of an ethyl group in the benzene ring. This is usually carried out by Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethyl halides (chloride or bromide), ethene or ethanol. The Lewis acid catalyst other than anhydrous AlCl3 used in this reaction are anhydrous FeCl3, SnCl4, BF3 etc.
Question 25. Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrates your answer by taking one example. (Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons)
Answer: For preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms, a mixture of two alkyl halides has to be used. Since they can react in three different ways, therefore, a mixture of three alkanes instead of desired alkane would be formed. Which cannot be separated by simple methods. For example, Wurtz reaction between 1-bromopropane and 1-bromobutane gives a mixture of three alkanes, i.e., hexane, heptane and octane.
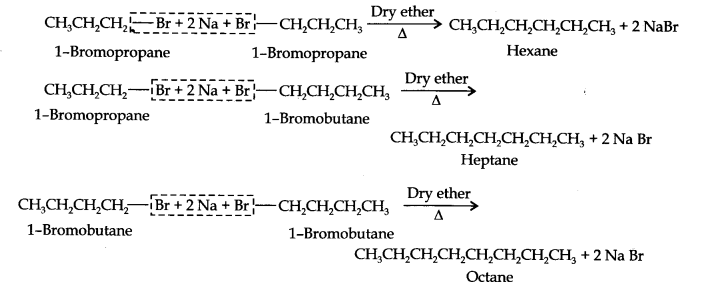
Conclusion of Ncert Solution of Hydrocarbons
Hereby, we have solved all the questions provided in the exercise of Hydrocarbons. We have used simple ways to explain the answer of all the 25 questions. This solutions will enhance the the ability and capacity to solve other questions of this chapter. We hope that you have liked this a little attempt. You are further requested to continue visit this website and share among your friends and favourites.

