Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf: Chemical equilibrium is the part of equilibrium. This is the 6th chapter of chemistry 11th. This chapter is very long hence we have decided to upload the solutions of this chapter in two parts as chemical equilibrium and Ionic equilibrium. In this part we shall solve all the questions of chemical equilibrium as given in the exercise of Ncert book. It is very essential to learn and solve the questions of this part because it will make easy and simple during solution of the next part.
Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf overview
Chemical equilibrium is the part of the chemistry in which we learn about the state of a process in which the properties like temperature, pressure, concentration of the system do not show any change with the passage of time. This state exists in chemical reaction then it is called chemical equilibrium.
Here we shall learn about law of mass actions, important factors which affect the rate of reaction, physical and chemical equilibrium, types of equilibrium. Besides we have to derive various formulas. Le Chattlier principle is also important part of this chapter. Application of equilibrium constant are also useful during solutions of the questions of exercise. Hence overall it can be said that this chapter is full of numerical questions.
Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf has been drafted in such a way that a good revision of this chapter can be done after solving all the questions of exercise. Hence don’t hesitate to perform your duties. Your every step will help to achieve your goal.
Questions and answers of chemical equilibrium
Q.1. A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour in a sealed container at a fixed temperature. The volume of the container is suddenly increased.
a) What is the initial effect of the change on vapour pressure?
b) How do rates of evaporation and condensation change initially?
c) What happens when equilibrium is restored finally and what will be the final vapour pressure? Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- (a) Initially, the vapour pressure will decrease because the same amount of vapour are now distributed in larger space.
(b) The rate of evaporation remains constant at constant temperature in a closed vessel. However, the rate of condensation will be low initially because there are fewer molecules per unit volume in the vapour phase and hence the number of collisions per unit time with the liquid surface decreases.
(c) When equilibrium is restored, rate of evaporation = rate of condensation. The final vapour pressure will be same as it was originally because vapour pressure of a liquid depends only on temperature not volume.
Q.2.What is Kc for the following equilibrium when the equilibrium concentration of each substance is: [SO2]= 0.60M, [O2] = 0.82M and [SO3] = 1.90M? Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
2SO2(g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2 SO3(g)
Ans:- Kc = [SO3]2/[SO2]2 [O2] = (1.90M)2 / (0.60M)2(0.82M) = 12.229 M–1 or 12.229 Lmol–1.
Q.3. At a certain temperature and total pressure of 105 Pa, iodine vapour contains 40% by volume of iodine atoms. I2(g)⇌2I (g) . Calculate KP for the equilibrium. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- Partial pressure of I (Iodine) atoms (p1) = 40/100 ×105 Pa = 0.4 × 105 Pa. Partial pressure of I2 (pI2) = 60/100 ×105 Pa = 0.6 × 105 Pa.
∴KP = pI2/pI2 = (0.4 × 105 Pa)2 /0.6 × 105 Pa = 2.67 × 104 Pa.
Q.4. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for each of the following reactions 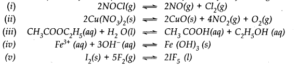
Ans:- 
Q.5. Find the value of Kc for each of the following equilibria from the value of K![]()
Ans:- (a) Δng = 3 – 2 = 1, KP = Kc(RT) or Kc = Kp/RT = 1.8 × 10–2/ 0.0831 × 500 = 4.33 × 10–4 (where R = 0.0831 bar litre mol–1K–1)
(b)Δng = 1 — 0 = 1, Kc = Kp/RT = 167/ 0.0831 × 1073 = 1.87
Q.6. For the following equilibrium, K =6.3 x 1014 at 1000 K. NO(g)+O3 —–>NO2(g) + O2(g) Both the forward and reverse reactions in the equilibrium are elementary bimolecular reactions. What is Kc for the reverse reaction? Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- For the reverse reaction, K’c = 1/ Kc = 1 / 6.3 × 1014 = 1.59 × 10–15
Question 7. Explain why pure liquids and solids can be ignored while writing the value of equilibrium constants. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- As we know that [Pure solid] = [Pure liquid] = No. of moles/ Volume in L = mass/mol.mass × 1/ volume = Mass /Volume × 1 /Mol.mass = Density/ Mol.mass. As density of a pure solid or pure liquid at constant temperature and molecular mass is always constant, therefore, their molar concentration are constant and included in the equilibrium constant.
Q.8. Reaction between nitrogen and oxygen takes place as follows:![]()
If a mixture of 0.482 mol of N2 and 0.933 mol of O2 is placed in a reaction vessel of volume 10 L and allowed to form N2O at a temperature for which Kc – 2.0 x 10-37, determine the composition of the equilibrium mixture. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- Suppose x mole of N2(g) reacts in the given reaction, x/2 moles of O2 (g) is used to produce X moles of N2O(g). The molar concentration of reactants and products at initial and at equilibrium can be represented in the following ways. 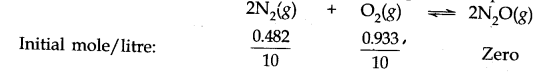
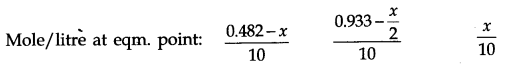
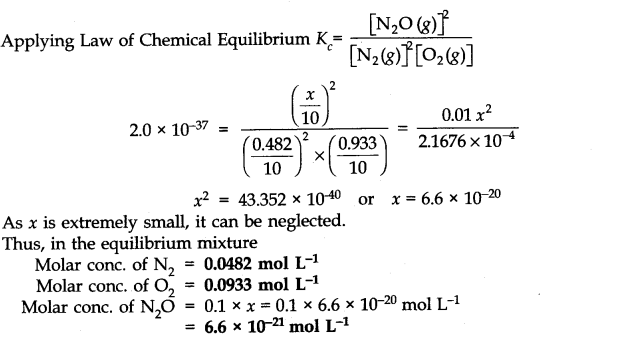
Q.9. Nitric oxide reacts with bromine and gives nitrosyl bromide as per reaction given below:![]()
When 0.087 mole of NO and 0.0437 mole of Br2 are mixed in a closed container at constant temperature, 0.0518 mole of NOBr is obtained at equilibrium. Determine the compositions of the equilibrium mixture. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- 0.0518 mol of NOBr is formed from 0.0518 mol of NO and 0.0518/2 mol of Br2. ∴ At equilibrium, Amount of NO = 0.087 – 0.0518 = 0.0352 mol. Again amount of Br2 = 0.0437 – 0.0259 = 0.0178 mol.
Q.10 ![]()
Ans:- For the given reaction, Δng = 2 – 3 = – 1 and KP = Kc(RT)Δn or Kc =Kp(RT)–Δn = = Kp(RT) = (2.0 × 1010 bar–1) (0.0831 bar litre mol–1K–1) (450 K) = 74.8 × 1010 Lmol-1 = 7.48 × 1011 Lmol-1sec-1
Q.11. A sample of HI (g) is placed in a flask at a pressure of 0.2 atm. At equilibrium partial pressure of HI (g) is 0.04 atm. What is Kp for the given equilibrium?![]()
Ans:- 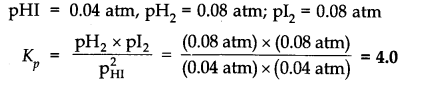
Q.12. A mixture of 1.57 mol of N2, 1.92 mol of H2 and 8.13 mol of NH3is introduced into a 20 L reaction vessel at 500 K. At this temperature, the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction![]()
Is this reaction at equilibrium? If not, what is the direction of net reaction?
Ans:- 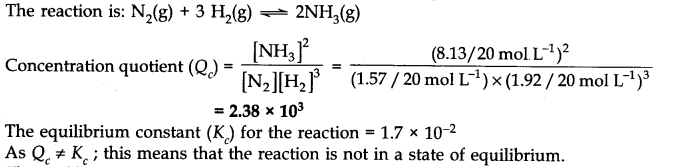
Q.13.The equilibrium constant expression for a gas reaction is,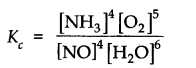
Write the balanced chemical equation corresponding to this expression. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) ⇌ 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g).
Q.14. If l mole of H20 and 1 mole of CO are taken in a 10 litre vessel and heated to 725 K, at equilibrium point 40 percent of water (by mass) reacts with carbon monoxide according to equation.![]()
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
Ans:- At equilibrium, [H2O] = (1 – 0.40) /10 mol L-1 = 0.06 mol L-1, [CO] = 0.06 mol L-1, [H2] = 0.4/10 mol L-1 = 0.04 mol L-1 , [CO2] = 0.04 mol L-1 ,
∴ Kc = [H2][CO2]/[H2O][CO] = 0.04 × 0.04/ 0.06 × 0.06 = 0.444
Q.15. At 700 K, equilibrium constant for the reaction H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI (g) is 54.8. If 0.5 mol L-1 of HI (g) is present at equilibrium at 700 K. What are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI (g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- 2HI (g) ⇌ H2(g) + I2(g), K = 1/54.8 At equilibrium, [HI] = 0.5 mol L-1 , [H2] = [I2] = x mol L-1 ∴ K = (x × x)/(0.5)2 = 1/54.8 (given). Now, x = 0.068 Hence, [H2] = [I2] = 0.068 mol L-1
Q.16. What is the equilibrium concentration of each of the substances in the equilibrium when the initial concentration of ICl was 0.78 M?![]()
Ans:-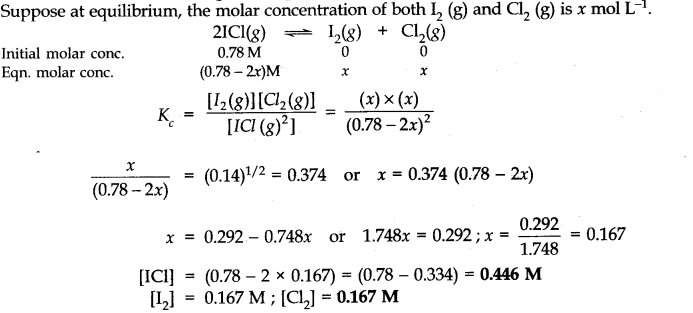
Q.17. K =0.04 atm at 898 K for the equilibrium shown below. What is the equilibrium concentration ok C2H6 when it is placed in a flask at 4 atm pressure, and allowed to come to equilibrium.![]()
Ans:- 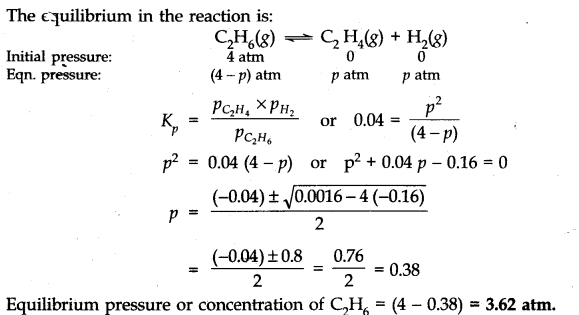
Q.18. The ester, ethyl acetate is formed by the reaction of ethanol and acetic acid and the equilibrium is represented as:
CH3COOH(l) + C2H5OH(l)→ CH3COOC2H5(l) + H2O(l)
(i) Write the concentration ratio (concentration quotient) Q for this reaction. Note that water is not in excess and is not a solvent in this reaction.
(ii) At 293 K, if one starts with 1.000 mol of acetic acid and 0.180 mol of ethanol, there is 0.171 mol of ethyl acetate in the final equilibrium mixture. Calculate the equilibrium constant. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
(iii) Starting mth 0.50 mol of ethanol and 1.0 mol of acetic acid and maintaining it at 293 K, 0.214 mol of ethyl acetate is found after some time. Has equilibrium been reached?
Ans:- 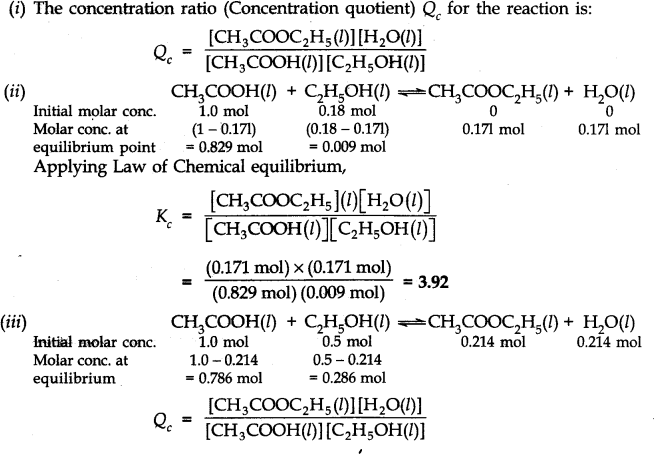
As QC ≠ Kc, equilibrium has not been attained.
Q.19. A sample of pure PCl5 was introduced into an evacuated vessel at 473 K. After equilibrium was reached, the concentration of PCl5 was found to be 0.5 x 10-1 mol L-1. If Kc is 8.3 x 10-3 what are the concentrations of PCl3 and Cl2 at equilibrium? Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- Suppose the initial concentration of PCl5 per litre = x mol
and concentration of PCl5 at equilibrium = 0.05 mol L-1
.’. Moles of PCl5 decomposed = (x – 0.05) mol
Moles of PCl3 formed = (x – 0.05) mol
Moles of Cl2 formed = (x – 0.05) mol
The molar concentration of reactants and products before the reaction and at the equilibrium state are: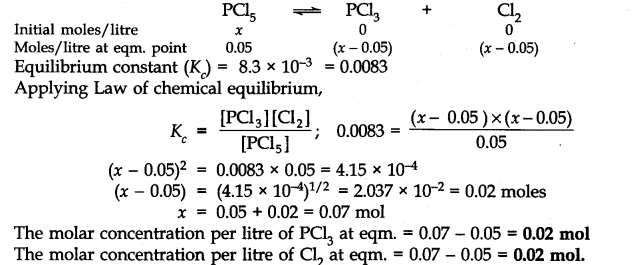
Q.20. One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron
(II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and C02
FeO(s) + CO(g) → Fe(s) + C02(g) ; Kp = 0.265 atm at 1050 K
What are the equilibrium partial pressures of CO and C02 at 1050 K if the initial pressures are: PCO = 1.4 atm and PCO2 = 0.80 atm?
Ans:-FeO(s) + CO(g) ⇌ Fe (s) + CO2(g) Initial pressure, [pCO] = 1.4 atm and [pCO2] = 0.80 atm ∴Qp = pCO2/pCO = 0.80/1.4 = 0.571
As Qp > Kp, reaction will move in the backward direction, that means pressure of CO2 will decrease and that of CO will increase to attain equilibrium. Hence, if p is the decrease in pressure of CO2, increase in pressure of CO = p. At equilibrium, pCO2 = (0.80 – p) atm and pCO = (1.4 + p) atm.
Now KP = pCO2/ pCO ∴ 0.265 = (0.80 – p)/(1.4 + p) or 0.265 (1.4 + p) = 0.80 – p or 1.265p = 0.429 or p = 0.339 atm ∴ At equilibrium pCO = 1.4 + 0.339 atm = 1.739 atm and pCO2 = 0.80 – 0.339 atm = 0.461 atm. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Q.21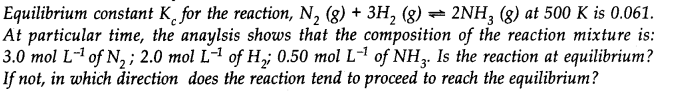
Ans:- Qc = [NH3]2/[N2][H2]3 = (0.5)2/(3.0)(2.0)2 = 0.0104, Here, Qc ≠ Kc, Hence, reaction is not in equilibrium. As Qc < Kc, reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
Q.22. Bromine monochloride (BrCl ) decomposes into bromine and chlorine and reaches the equilibrium:![]()
The value of Kc is 32 at 500 K. If initially pure BrCl is present at a concentration of 3.3 x10-3mol L-1what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium?
Ans:- If x moles of BrCl decomposes till equilibrium, the molar concentration of reactants and products at initial state and equilibrium state can be represented in the following ways by chemical equation. 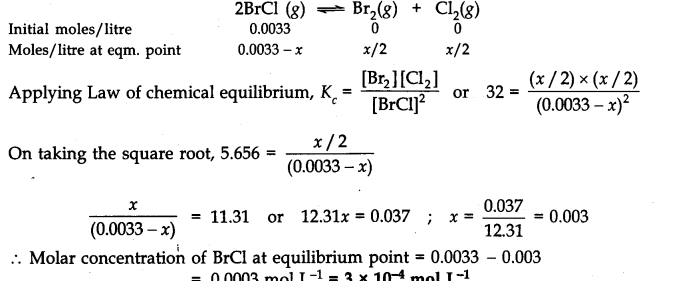
Q.23. At 1127 K and 1 atmosphere pressure, a gaseous mixture of CO and C02 in equilibrium with solid carbon has 90.55% CO by mass. ![]()
Calculate Kc for the reaction at the above temperature. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- 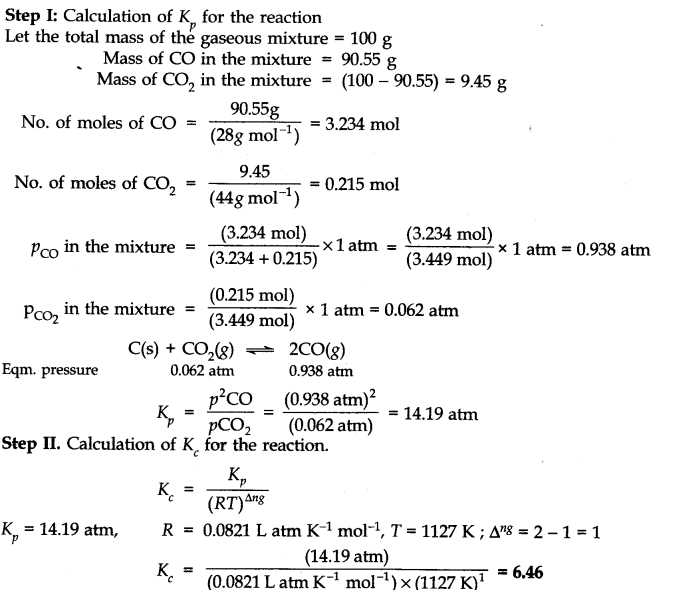
Q.24. Calculate (a) ∆G– and (b) the equilibrium constant for the formation of N02 from NO and 02 at 298 K 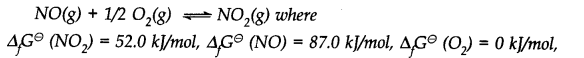
Ans:- 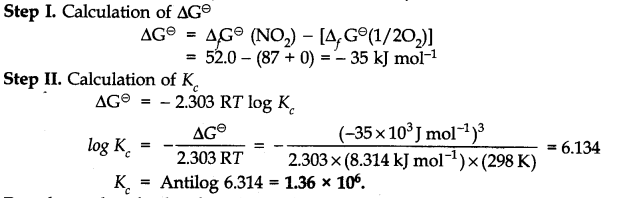
Q.25. Does the number of moles of reaction products increase, decrease or remain same when each of the following equilibria is subjected to a decrease in pressure bp increasing the volume?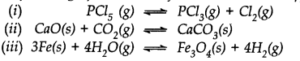
Ans:- Applying Le Chatelier’s principle, on decreasing the pressure, moles of reaction products will (a) increase (b) decrease (c) remain same (np = nr gaseous).
Q.26. Which of the following reactions will get affected by increase in pressure ? Also mention whether the change will cause the reaction to go to the right or left direction.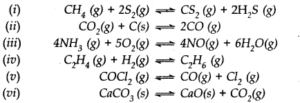
Ans:- Those reactions will be affected by increasing the pressure in which (np ≠ nr gaseous ). Hence reaction (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) and (vi) will be affected. By applying, Le Chatelier’s principle, we can predict the direction in the following way:
(i) np = 3, nr = 3 i.e., np = nr, reaction will not be affected by pressure.
(ii) np = 2, nr = 1 i.e., np > nr, reaction will go in the backward direction.
(iii) np = 10, nr =9 i.e., np > nr, reaction will go in the backward direction.
(iv) np = 1, nr =2 i.e., np < nr, reaction will go in the forward direction.
(v) np = 2, nr =1 i.e., np > nr, reaction will go in the backward direction.
(vi) np = 1, nr =0 i.e., np > nr, reaction will go in the backward direction. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Q.27. The equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 1.6 x 105at 1024 K.
Find the equilibrium pressure of all gases if 10.0 bar of HBr is introduced into a sealed container at 1024 K.![]()
Ans:-
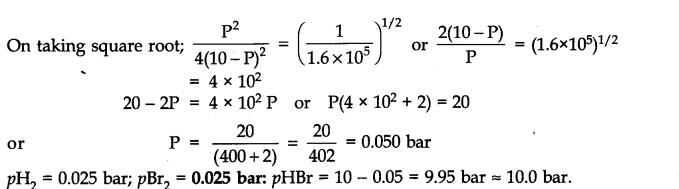
Q.28. Hydrogen gas is obtained from the natural gas by partial oxidation with steam as per the following endothermic reaction:![]()
Write the expression for Kp for the above reaction
How will the value of Kp and composition of equilibrium mixture be affected by:
(i) increasing the pressure, (ii) increasing the temperature, (iii) using a catalyst? Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- (a) Kp = (pCO × p3H2)/(pCH4 × pH2O) (b) (i) According to the Le Chatelier’s principle, equilibrium will shift in the backward direction.
(ii) As the given reaction is endothermic, by Le Chatelier’s principle, equilibrium will shift in the forward direction.
(iii) Equilibrium composition will not be disturbed but equilibrium will be attained quickly.
Q.29. What is the effect of:
(i) addition of H2 (ii) addition of CH3OH
(iii) removal of CO (iv) removal of CH3OH![]()
Ans:- (i) Equilibrium will shift in the forward direction. (ii) Equilibrium will shift in the backward direction. (iii) Equilibrium will shift in the backward direction. (iv) Equilibrium will shift in the forward direction. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Q.30. At 473 K, the equilibrium constant Kc for the decomposition of phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is 8.3 x 10-3 . if decomposition proceeds as:![]()
(a) Write an expression for Kc for the reaction
(b) What is the value of Kc for the reverse reaction at the same temperature.
(c) What would be the effect on Kc if
(i) More of PCl5is added (ii) Temperature is increased.
Ans:- (a) Kc = [PCl3 (g)][Cl2(g)] / [PCl5 (g)] (b) K’ = 1/Kc = 1/8.3 × 10–3 = 120.48 (c) (i) No effect as Kc is constant at constant temperature. (ii) NO effect (iii) As given reaction is endothermic, on increasing the temperature, Kf will increase As Kc = Kf / Kb. Kc will increase with increase of temperature.
Q.31. Dihydrogen gas used in Haber’s process is produced by reacting methane from natural gas with high temperature steam. The first stage of two stage reaction involves the formation of CO and H2 In second stage, CO formed in first stage is reacted with more steam in water gas shift reaction.![]()
If a reaction vessel at 400°C is charged with an equimolar mixture of CO and steam so that PCO = PH2O = 4.0 bar, what will be the partial pressure of H2 at equilibrium? Kp = 0.1 at 400°C. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Ans:- 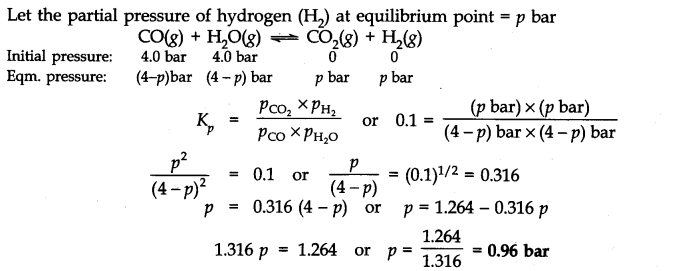
Q.32. Predict which of the following will have appreciable concentration of reactants and products: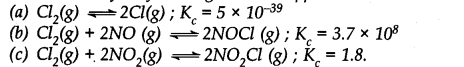
Ans:- The answer will be (c) because for reaction (c), the value of Kc is neither high nor low that means reactants and products will be present in comparable amounts.
Q.33.The value of Kc for the reaction 302(g) —>203(g) is 2.0 x 10-50 at 25°C. If equilibrium concentration of 02 in air at 25°C is 1.6 x 10-2, what is the concentration of O3?
Ans:- For the given reaction Kc = [O3]2/[O2]3 ∴ 2.0 × 10–50 = [O3]2/(1.6 × 10–2) or [O3]2 = (2.0 × 10–50)(1.6 × 10–2)3 = 8.192 × 10–56 or [O3] = 2.86 × 10–28 M. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Q.34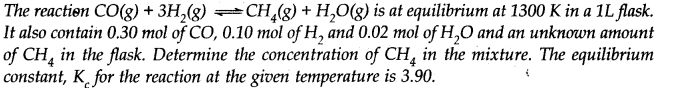
Ans:- For the given reaction in the question Kc = [CH4][H2O]/[CO][H2]2 ∴ 3.90 = [CH4][0.02]/(0.30)(0.10)2 [Here, molar concentration = No. of moles because Volume of flask = 1 L]. Now [CH4] = 0.0585 M = 5.85 × 10–2 M. Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
Conclusion of Ncert solutions of chemical equilibrium class 11 pdf
We have solved all the questions of chemical equilibrium given in the exercise in proper way. All the concepts of this chapter have been applied during solution of these problems. There are 34 questions of this chapter. The applied topics are equilibrium constant in terms of concentration and pressure and their relationship, characteristics and applications of equilibrium constant and Le Chatelier’s principle.
We hope you must have learned and liked this content. Therefore we shall request you to share this article among your friends and favourites. Thanks for coming to this website.

