Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids: This is the most important chapter of chemistry. We shall learn and revise many useful reactions which are applied in preparation and properties of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acid. Each and every questions of this chapter are important for the students who are preparing for the 12th board exams, Neet, Jee(mains), IIT advance and competitive exams. Therefore, we must solve all the Intext and exercise questions of this chapter.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids are compounds which have many uses in our daily life. As we know that formalin is used as a disinfectant and germicide. Formalin is a 40% solution of formaldehyde in water. Bakelite is a very useful polymer made of Phenol and formaldehyde. They are widely used as a flavouring agents and in the manufacture of dyes. Methanal is used in leather industry for tanning hides and as a reducing agent in silvering of mirrors.
Learning Objectives in Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids
- How to write the common and IUPAC names of Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids.
- To write the structures of compounds containing functional groups in carbonyl and carboxylic compounds.
- To describe the important methods of preparation and reactions of these compounds.
- To correlate physical properties and chemical reactions of Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids, with their structures.
- To explain the mechanism of a few selected reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.
- To understand various factors affecting the acidity of carboxylic acids and their reactions.
- To describe the Uses of Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids.
Answers of Intext questions in Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids
Question 1. Write the structures of the following compounds:
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-OxopentanaI
(v) Di-sec.butylketone
(vi) 4-fluoroaeetophenone
Answer: 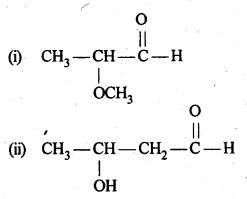
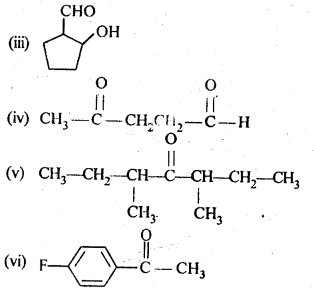
Question 2. Write the structures of the products of the following reactions:
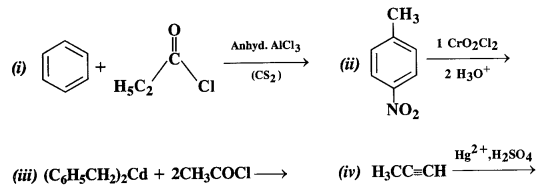
Answer: 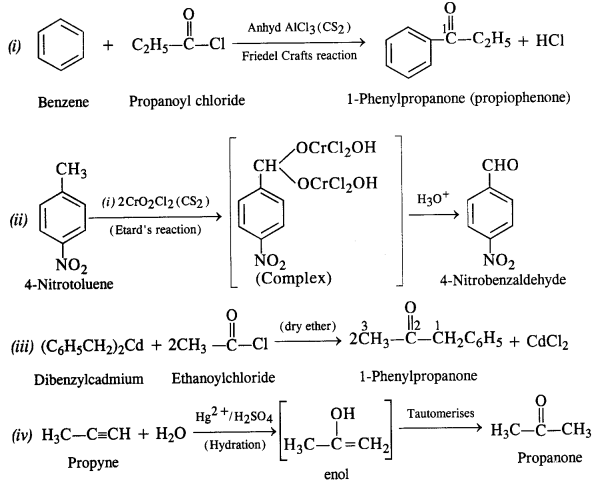
Question 3. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3
Answer: The order of boiling points is : CH3CH2CH3 < CH3OCH3 < CH3CHO <CH3CH2OH
All these compounds have comparable molecular masses. But CH3CH2OH undergoes extensive intermolecular H-bonding and thus its b.pt. is the highest. CH3CHO is more polar than CH3OCH3 so that dipole-dipoie interactions in CH3CHO are greater than that is in CH3OCH3. Thus, b.pt. of CH3CHO > CH3OCH3. CH3CH2CH3 has only weak van der waals forces between its molecules and hence has the lowest b.pt.
Question 4. Arrange the following carbonyl compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions :
(a) Ethanal, propanal, propanone, butanone
(b) Benzaldehyde, p-tolualdehyde, p-nitrobenzaldehyde, acetophenone.
Answer: (a) The increasing order of the reactivity of the carbonyl compounds towards nucleophilic addition reactions is as follows :
butanone < propanone < propanal < ethanal
This reactivity is based upon two factors. These are steric hindrance and electronic configuration.
(b) The increasing order of reactivity is as follows :
acetophenone < p-tolualdehyde < benzaldehyde < p-nitrobenzaldehyde
Explanation: Acetophenone is a type of ketone that is the least reactive towards nucleophilic addition. The remaining are aldehydes. Among them, p-tolualdehyde is less reactive than benzaldehyde due to the presence of CH3 group at the para position w.r.t. -CHO group which will increase the electron density on the carbonyl carbon atom due to hyper conjugation effect. As a result, the nucleophile attack takes place to a lesser extent as compared to benzaldehyde.
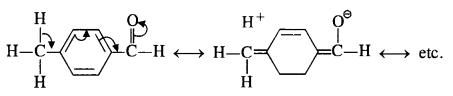
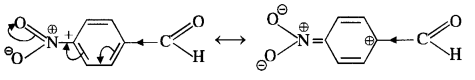
In p-nitrobenzaldehyde, the nitro group is electron withdrawing in nature due to -I effect as well as -R effect. As a result The electron density on the carbonyl carbon atom decreases and hence, favours the nucleophile attack.
Question 5. Predict the products of the following reactions: 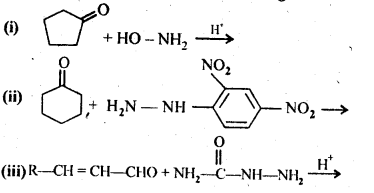
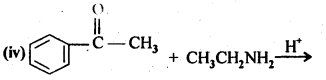
Answer: 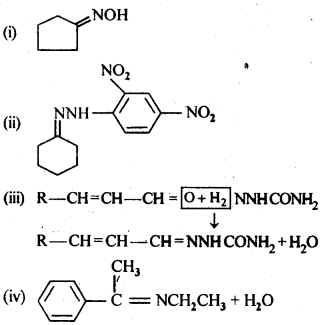
Question 6. Give the 1UPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) PhCH2CH2COOH
(ii) (CH3)2 C=CHCOOH 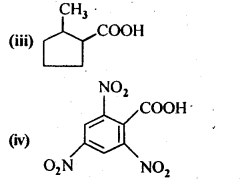
Answer: (i) 3 – Phenylpropanoic acid
(ii) 3 – Methylbut-2-enoic acid
(iii) 2-Methylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
(iv) 2,4,6 – Trinitrobenzoic acid
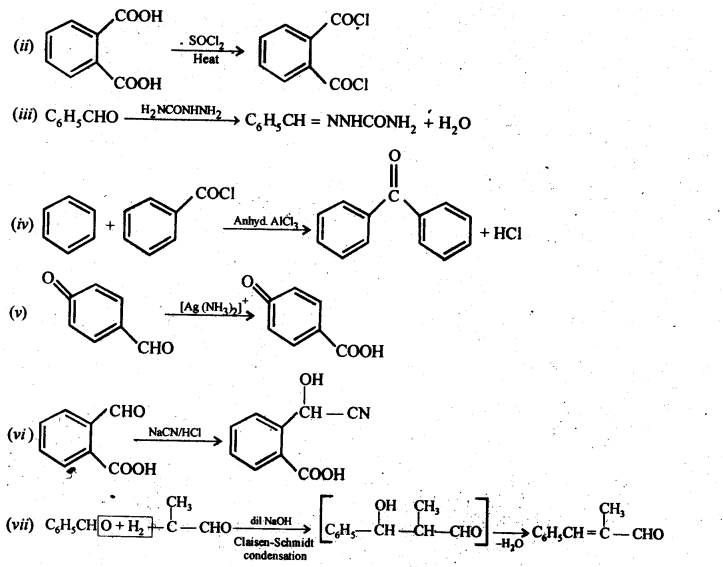
Question 7. Show how each of the following compounds can be converted into benzoic acid.
(i) Ethylbenzene
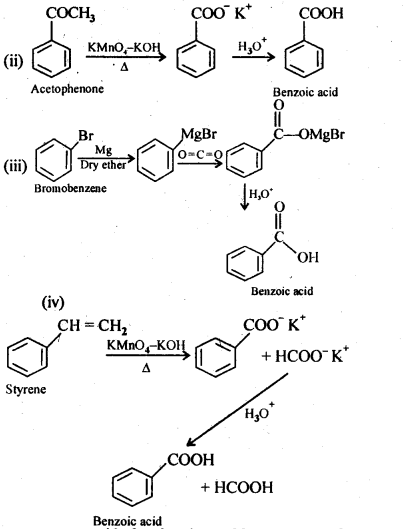
(ii) Acetophenone
(iii) Bromobenzene
(iv) Phenylethene (styrene)
Answer: 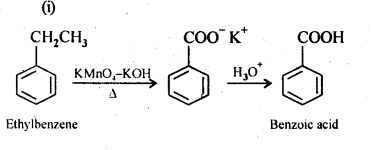
Question 8. Which acid from each of the following pairs would you expect to be a stronger acid?
(i) CH3COOH or CH2FCOOH
(ii) CH2FCOOH or CH2ClCOOH
(iii) CH2FCH2CH2COOH or CH3CHFCH2COOH 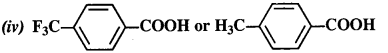
Answer: Explanation: CH3 group due to +I effect increases the electron density on the oxygen atom in O – H bond in the carboxyl group as a result the cleavage of bond becomes difficult. Therefore, the acidic strength decreases. The F atom has very strong -I effect, i.e., electron withdrawing effect. It decreases the electron density on the oxygen atom and hence the cleavage of bond becomes easier. The acidic character therefore, increases. It can be further related as follows:
- No. of F- atoms present in the molecule.
- Relative position of the F atom in the carbon atom chain.
In the light of the above discussion we can say that:
(i) CH2FCOOH is a stronger acid.
(ii) CH2FCOOH is a stronger acid.
(iii) CH3CHFCH2COOH is a stronger acid. 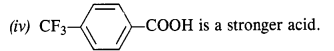
Answer of Exercise questions in Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic acids
Question 1. What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
(i) Cyanohydrin (ii) Acetal
(iii) Semicarbazone (iv) Aldol
(v) Hemiacetal (vi) Oxime
(vii) Ketal (viii) Imine (ix) 2,4-DNP derivative (x) Schiff’s base.
Answer: (i) Cyanohydrin: Those organic compounds which possess hydroxyl and cyanide groups on the same carbon atom are called cyanohydrins.These compounds are formed by addition of HCN to aldehydes or ketones in a weakly basic medium. ![]()
(ii) Acetal or gem – Dialkoxy compounds: Those compounds in which the two alkoxy groups are present on the terminal carbon atom are called acetals. These are formed by the action of an aldehyde with two gram equivalents of a monohydric alcohol in presence of dry HCl gas. 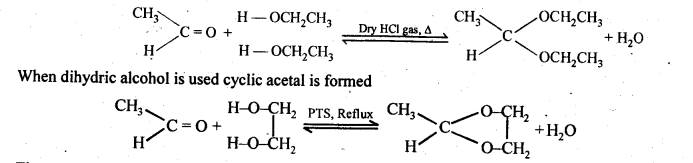
(iii) Semicarbazones are the derivatives of aldehydes and ketones. These are produced by action of semicarbazide on them in acidic medium. 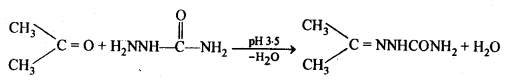
(iv) Aldols are P-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones and they are produced after the condensation of two molecules of the same or different aldehydes and / or ketones in presence of a dilute aqueous base like NaOH or Ba(OH)2. For example, 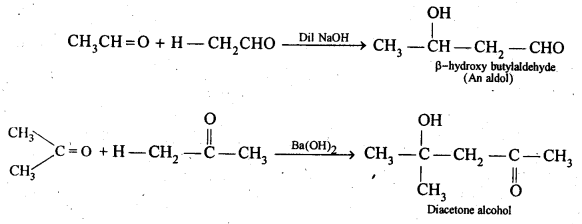
(v) Hemiacetal: gem – Alkoxyalcohols are known as hemiacetals. These are formed by the addition of one molecule of a monohydric alcohol with an aldehyde in the presence of dry HCl gas.
(vi) Oximes are formed when aldehydes or ketones react with hydroxyl amine in weakly acidic medium. 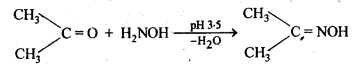
(vii) Ketals are produced when a ketone is reacted with dihydric alcohols like ethylene glycol in the presence of dry HCl gas or /p-toluene sulphonic acid (PTS). 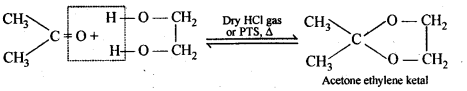
Ketals are easily hydrolysed by dilute mineral acids to regenerate the original ketones. Therefore, ketals are used for protecting keto groups in organic synthesis.
(viii) Those compounds which contain -C = N – group are called imines. They are produced when aldehydes and ketones react with ammonia derivatives. ![]()
(ix)2, 4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazone (i.e., 2,4-DNP derivatives) are produced when aldehydes or ketones react with 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine in weakly acidic medium. 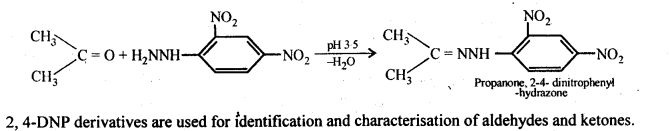
(x) When aldehydes and ketones react with primary aliphatic or aromatic amines, azomethines or SchifFs bases are formed. 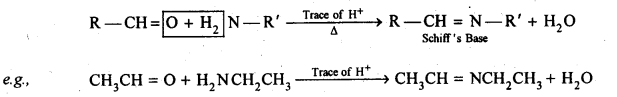
Question 2. Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
(i) CH3CH (CH3)—CH2 CH2—CHO
(ii) CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2CH2Cl
(iii) CH3CH=CHCHO
(iv) CH3COCH2COCH3
(v) CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2COCH3
(vi) (CH3)3CCH2COOH.
(vii) OHCC6H4CHO-p
Answer: (i) 4-Methyl pentanal
(ii) 6-Chloro-4-ethylhexan-3-one
(iii) But-2-en-l-al
(iv) Pentane-2,4-dione
(v) 3,3,5-Trimethyl-hexan-2-one
(vi) 3,3-Dimethyl butanoic acid
(vii) Benzene-1,4-dicarbaldehyde
Question 3. Draw the structures of the following compounds.
(i) 3-Methylbutanal
(ii) p-Methylbenzaldehyde
(iii) 4-Chloropentan-2-one
(iv) p, p’-Dihydroxybenzophenone
(v) p-Nitropropiophenone
(vi) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one.
(vii) 3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
(viii) Hex-2-en-4-ynoic acid
Answer: 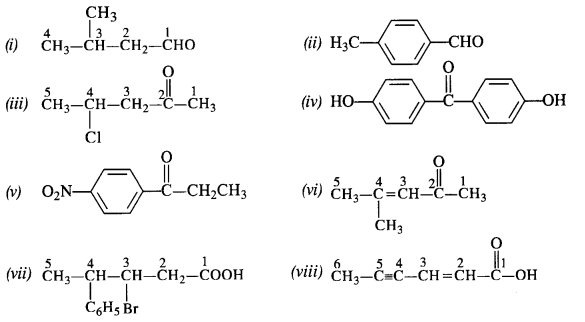
Question 4. Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names.
(i) CH3CO(CH2)4CH3
(ii) CH3CH2CH BrCH2CH(CH3)CHO
(iii) CH3(CH2)5CHO
(iv) Ph—CH=CH—CHO 
Answer: 
Question 5. Draw structures of the following derivatives:
(i) The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
(ii) Cyclopropanone oxime
(iii) Acetaldehydedimethylacetal
(iv) The semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
(v) The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
(vi) The methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde
Answer: 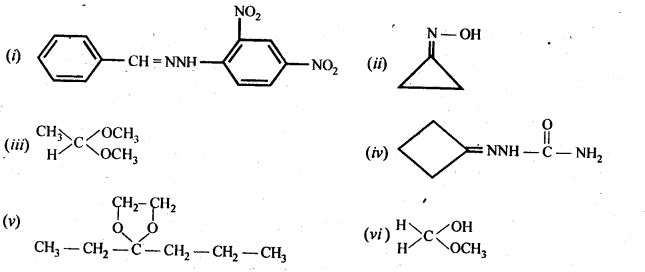
Question 6. Predict the product when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with following reagents :
(i) C6H5MgBr followed by H30+
(ii) Tollen’s reagent
(iii) Semicarbazide in the weakly acidic medium
(iv) Excess of ethanol in the presence of acid
(v) Zinc amalgam and Cyclohexanecarbaldehyde Semicarbazide
Answer: 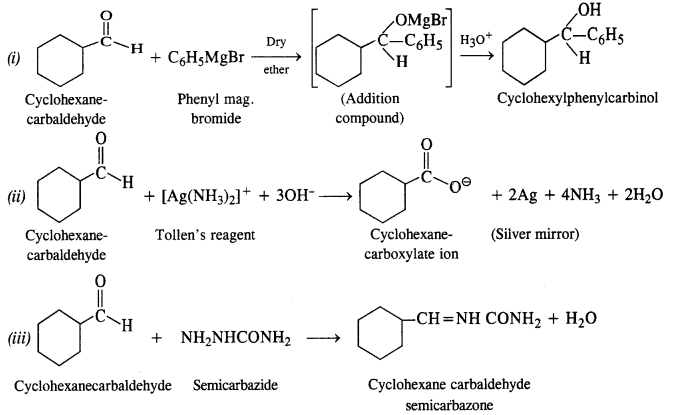
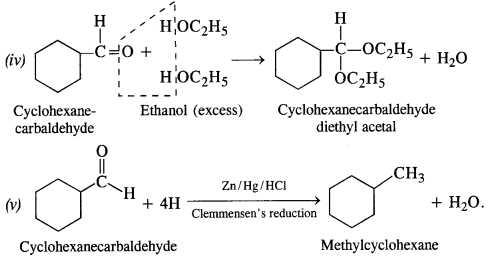
Question 7. Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither? Write the structures of the expected products of aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction.
(i) Methanal
(ii) 2-Methylpentanal
(iii) Benzaldehyde.
(iv) Benzophenone
(v) Cyclohexanone
(vi) 1-Phenylpropanone
(vii) Phenylacetaldehyde
(viii) Butan-l-ol 1
(ix) 2,2-Dimethylbutanal
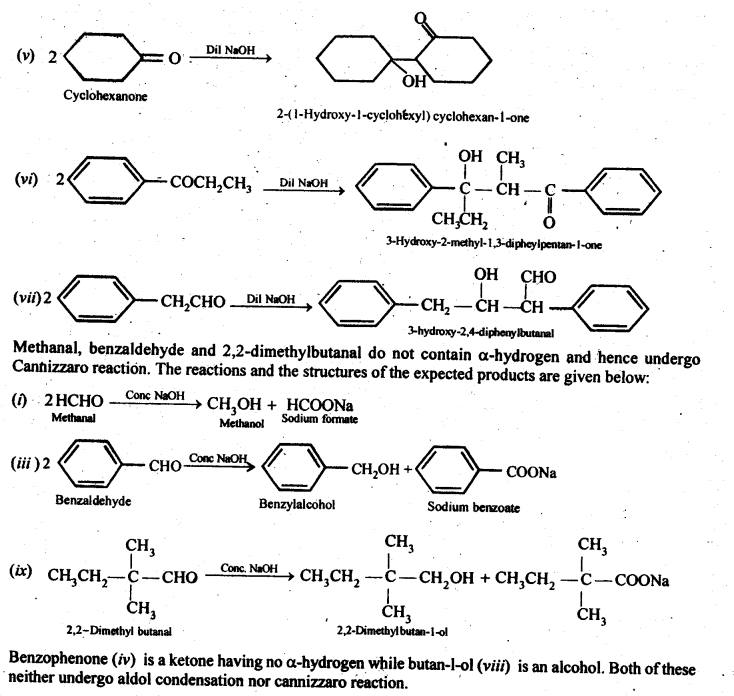
Answer: 2-Methylpentanal, cyclohexanone, 1-phenylpropanone and phenylacetaldehyde contain one or more α-hydrogen and hence they undergo aldol condensation. The possible reactions and the structures of the expected products are given below: 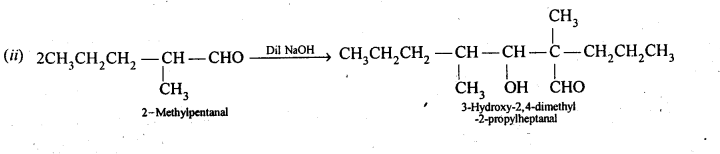
Question 8. How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds?
(i) Butane-1,3-diol
(ii) But-2-enal
(iii) But-2-enoic acid
Answer: 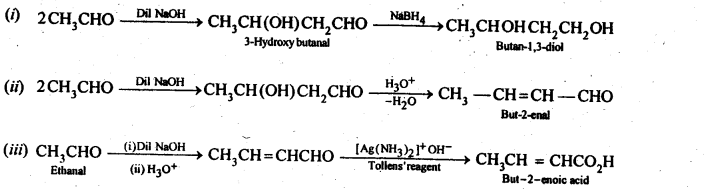
Question 9. Write structural formulas and names of four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde acts as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
Answer: 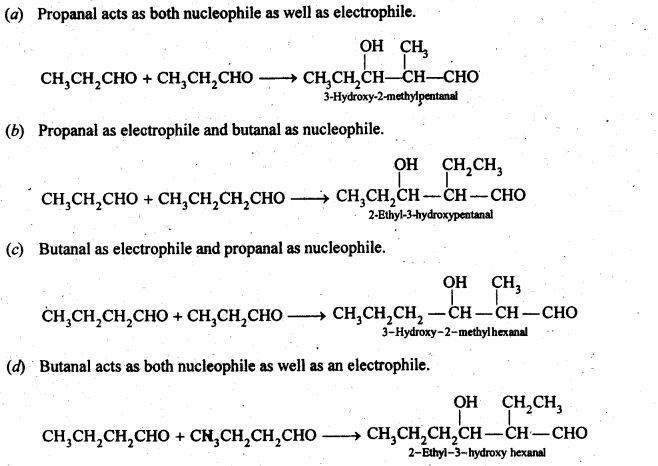
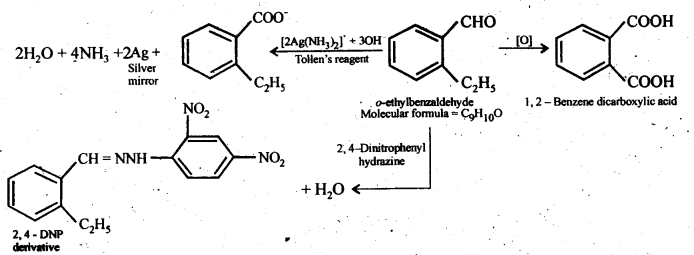
Question 10. An organic compound with the molecular formula C9H10O forms 2,4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent, and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer: The compound with molecular a formula C9H10O forms a 2,4-DNP derivative and reduces Tollen’s reagent, This tendency justifies that it must be an aldehyde. Since it undergoes Cannizzaro reaction also, therefore, it can be realized that CHO group is directly attached to the benzene ring.
Again on vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzene dicarboxylic acid, therefore, it can be optimized that it must be an ortho- substituted benzaldehyde. The only o-substituted aromatic aldehyde having molecular formula C9H10O is o-ethyl benzaldehyde. All the reactions can be explained on the basis of the following structures.
Question 11. An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B} and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (Q on dehydration gives but-l-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
Answer: According to the question an organic A with molecular formula C8H16O2 upon hydrolysis gives carboxylic acid B and the alcohol C and oxidation of C with chromic acid again produces the acid B, that means, both the carboxylic acid B and alcohol C must have the same number of carbon atoms. Further, ester A contains eight carbon atoms, therefore, both the carboxylic acid B and the alcohol C must have four carbon atoms each.
When the alcohol C on dehydration gives but-l-ene, therefore, this alcohol must be a straight chain, i.e., butan-l-ol. If C is butan-l-ol, then the acid B must be butanoic acid and the ester A must be butyl butanoate. All above can be understood by the following chemical equations.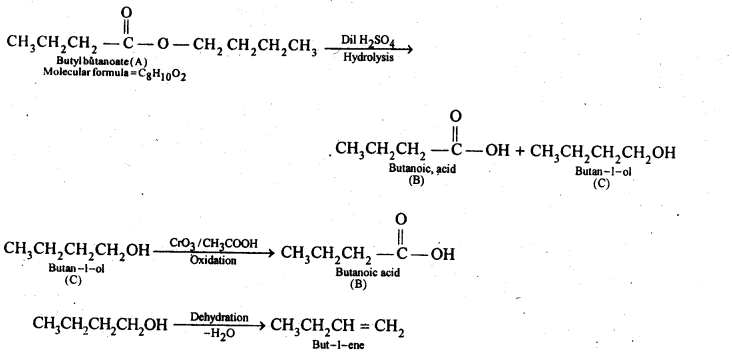
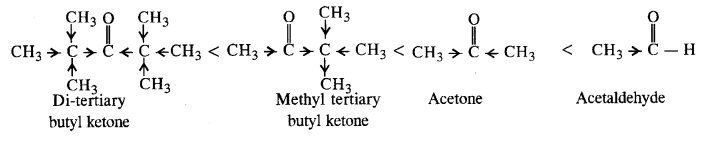
Question 12. Arrange the following in increasing order of the property indicated :
(i) Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di tert. butyl ketone, Methyl tert. butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN).
(ii) CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength)
(iii) Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3, 5-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
Answer: (i) Cyanohydrin derivatives are formed when the nucleophile (CN– ion) attacks on the carbon atom of the carbonyl group. The order of reactivity is as follows:
- The reactivity decreases with increase in +I effect of the alkyl group.
- The reactivity decreases with increase in steric hindrance due to the size as well as number of the alkyl groups. According to the above information, the decreasing order of reactivity can be as follows:
(ii) Since the alkyl group with +I effect decreases the acidic strength. The +I effect of isopropyl group will be more than that of n-propyl group. Similarly, bromine (Br) with -I-effect increases the acidic strength. Again the closer is its position in the carbon atom chain w.r.t., carboxyl (COOH) group, The more will be its -I-effect and stronger will be the acid. Hence, the increasing order of acidic strength will be as follows:
(CH3)2CHCOOH< CH3CH2CH2COOH < CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH < CH3CH2CH(Br) COOH
(iii) As we know that the electron donating group (OCH3) decreases the acidic strength of the benzoic acid. At the same condition, the electron withdrawing group (N02) increases the acidic strength. On the basis of this concept, the increasing order of acidic strength will be as follows : 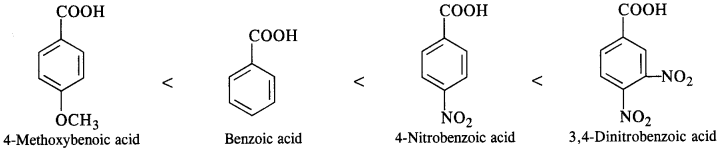
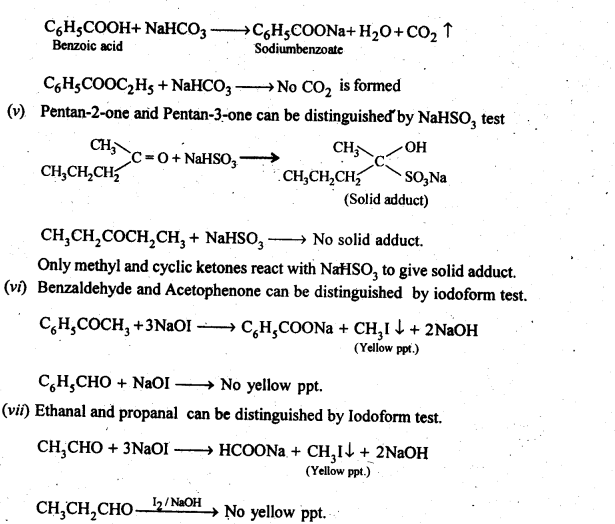
Question 13. Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
(i) Propanal and Propanone
(ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(iv) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
(v) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(vi) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.
(vii) Ethanal and Propanal
Answer: 
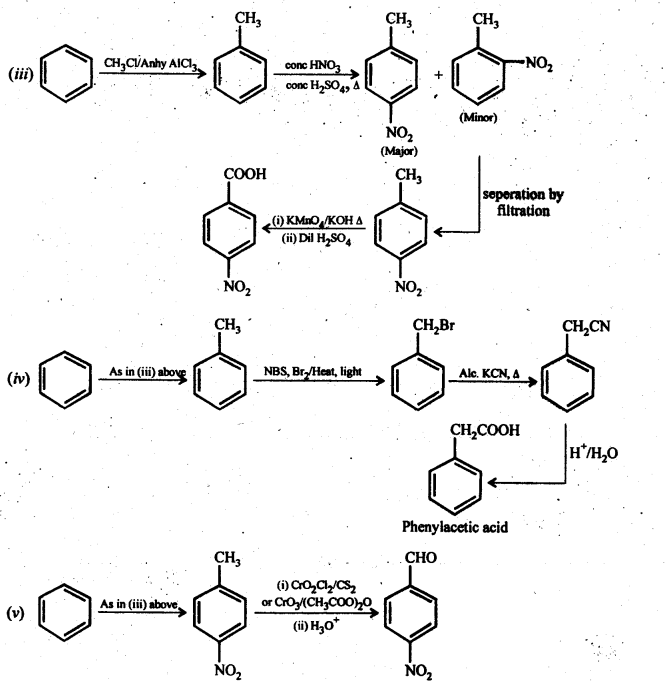
Question 14. Row will you prepare the following compounds from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
(i) Methyl benzoate
(ii) m-nitrobenzoic acid
(iii) p-nitrobenzoic acid
(iv) Phenylacetic acid
(v) p-nitrobenzaldehyde
Answer: 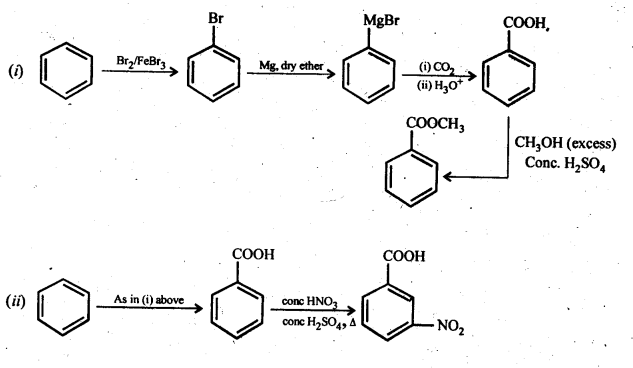
Question 15. How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
(i) Propanone to Propene
(ii) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
(iii) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iv) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
(v) Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone –
(vi) Bromobenzene to 1-PhenylethanoL
(vii) Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol. (viii) Benzaldehyde to α Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
(ix) Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzy -1- alcohol
Answer: 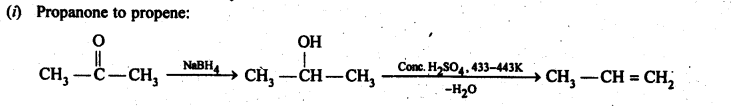
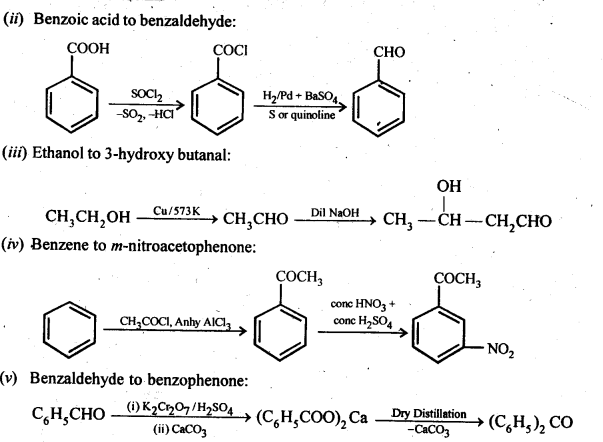
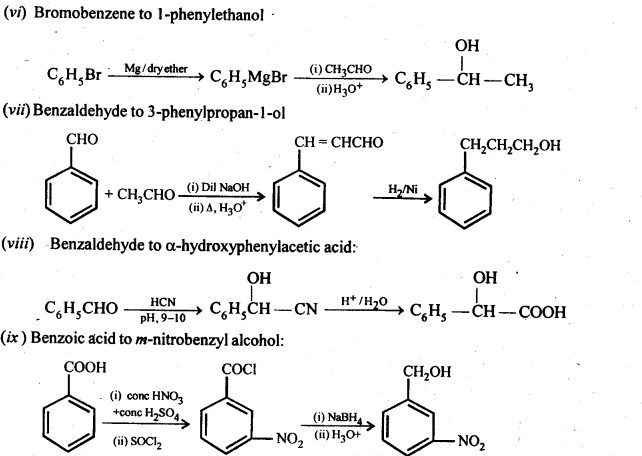
Question 16. Describe the following:
(i) Acetylation
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
(iii) Cross aldol condensation
(iv) Decarboxylation
Answer: (i) Acetylation is a process in which an acetyl group is introduced into a compound named as the substitution of an acetyl group for an active hydrogen atom. This process is usually carried out in presence of a base such as pyridine, dimethylaniline, etc. ![]()
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction : Aldehydes which do not contain an α-hydrogen atom, when treated with concentrated alkali solution undergo disproportionation, i.e., self oxidation reduction. As a result, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol at the cost of the other which is oxidised to the corresponding carboxylic acid. This reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction. 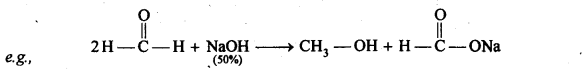
(iii) Cross aldol condensation: Aldol condensation between two different aldehydes is called cross aldol condensation. If both aldehydes contain α-hydrogen atoms, It gives a mixture of four products. 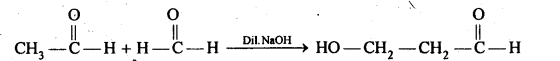
(iv) Decarboxylation: The process of removal of a molecule of CO2 from a carboxylic acid is called decarboxylation. Sodium salts of carboxylic acids when heated with soda-lime undergoes decarboxylation to yield alkanes. ![]()
Question 17. Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products.
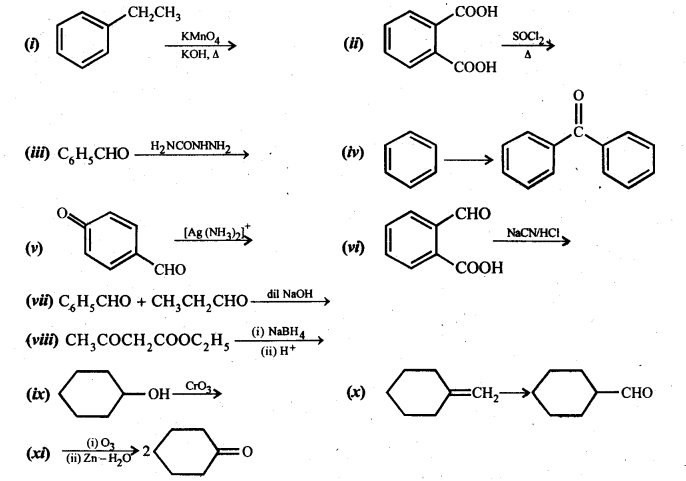
Answer: 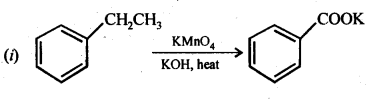
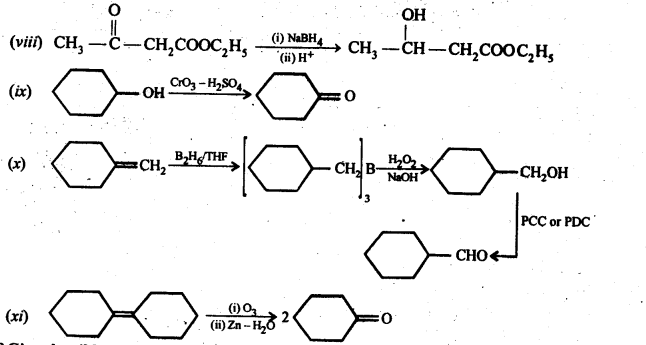
Question 18. Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
(i) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6 trimethylcyclohexanone does not
(ii) There are two – NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(iii)During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as soon as it is formed.
Answer: 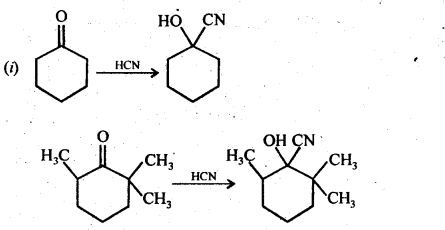
As it looks that the yield of second reaction is very low due to the presence of three methyl groups at α-positions with respect to the C = O, They cause hindrance as a result the nucleophilic attack by the CN– ion does not occur . While, there is no such steric hindrance in cyclohexanone, therefore, nucleophilic attack by the CN– ion occurs easily and hence cyclohexanone cyanohydrin is produced in good yield.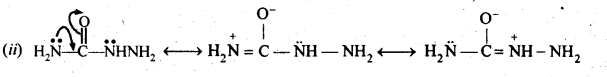
Although semicarbazide has two – NH2 groups but one of them (i.e., which is directly attached to C = O) is involved in resonance as shown above. As a result, electron density on N of this -NH2 group decreases and hence it does not act as a nucleophile. In contrast, the other -NH2 group (i.e.. attached to NH) is not involved in resonance and hence lone pair of electrons present on N atom of this -NH2 group is available for nucleophilic attack on the C = O group of aldehydes and ketones.’
(iii) The formation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in presence of an acid catalyst is a reversible reaction. ![]()
Thus to shift the equilibrium in the forward direction, the water or the ester formed should be removed as fast as it is formed.
Questions 19. An organic compound contains 69-77% carbon, 11-63 % hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogensulphite and give positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation, it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Write the possible structure of the compound.
Answer: 
Since the compound form sodium hydrogen sulphite addition product, therefore, it must be either an – aldehyde or methyl/ cyclic ketone. Since the compound does not reduce Tollens’ reagent therefore, it cannot be an aldehyde. Since the compound gives positive iodoform test, therefore, the given compound is a methyl ketone. Since the given compound on vigorous oxidation gives a mixture of ethanoic acid and propanoic acid, therefore, the methyl ketone is pentan-2-one, i.e.,
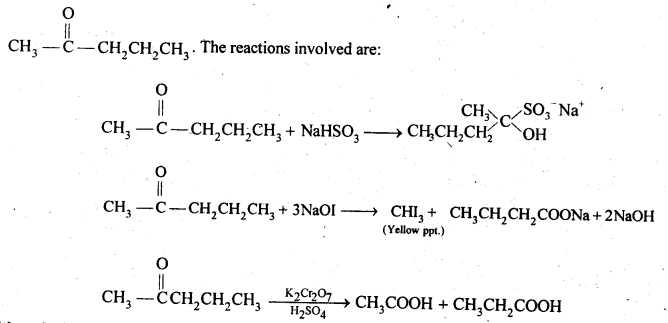
Question 20. Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than on phenol. Why?
Answer: Consider the resonating structures of carboxylate ion and phenoxide ion. 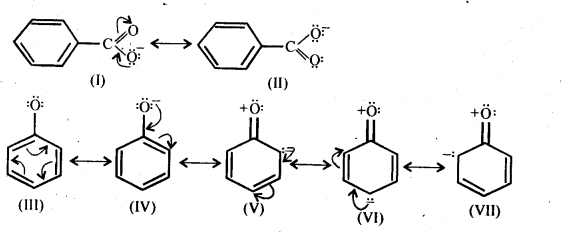
In case of phenoxide ion, structures (V – VII) carry a negative charge on the less electronegative carbon atom. Therefore, their contribution towards the resonance stabilization of phenoxide ion is very small.
In structures I and II, (carboxylate ion), the negative charge is delocalized over two oxygen atoms while in structures III and IV, the negative charge on the oxygen atom remains localized only the electrons of the benzene ring are delocalized. Since delocalization of benzene electrons contributes little towards the stability of phenoxide ion therefore, carboxylate ion is much more resonance stabilized than phenoxide ion.
Thus, the release of a proton from carboxylic acids is much easier than from phenols. In other words, carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenols.
