Introduction
Heat is a form of energy that makes substances hot or cold. The sensation of hotness or coldness is measured using temperature. In this chapter, we will study the concept of heat, temperature, methods of heat transfer, and practical applications in our daily lives.
Heat and Temperature
What is Heat?
- Heat is a kind of energy that can flow from a hot thing to a cold thing.
- SI unit of heat: Joule (J).
What is Temperature?
- Temperature is used to measure the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
- Device used: Thermometer.
- Common units: Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), Kelvin (K).
✅ Exam Tip: Temperature is not heat; it only indicates how hot or cold something is.
Measuring Temperature
Laboratory Thermometer
- Used in laboratories to measure temperature.
- Range: –10°C to 110°C.
- Precautions:
- Bulb should not touch the surface of container.
- Keep upright, not tilted.
Clinical Thermometer
- This thermometer is used by doctors to measure human body temperature.
- Range: 35°C to 42°C (or 94°F to 108°F).
- Normal body temperature: 37°C (98.6°F).
Transfer of Heat
Heat can move from one place to another in three ways:
1. Conduction
- Heat transfer through solids (particle-to-particle).
- Example: A metal spoon becomes hot when placed in hot tea.
- Good conductors: Metals (copper, aluminum, iron).
- Poor conductors (Insulators): Wood, plastic, rubber.
2. Convection
- Heat transfer in liquids and gases by movement of particles.
- Example:
- Heating water in a pot (hot water gets rise and cold water gets down).
- Sea breeze and land breeze are caused by convection.
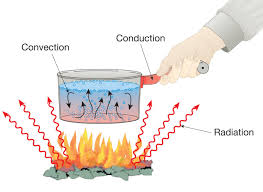
3. Radiation
- Heat transfer without a medium, in the form of electromagnetic waves.
- Example: Heat from the Sun reaches the Earth.
- Black objects absorb more heat than white or shiny objects.
Applications of Heat Transfer
- Cooking: Utensils are made of metals for conduction.
- Buildings: Houses in hot areas are painted white to reflect heat.
- Woolen Clothes: Wool traps air, reducing heat loss in winter.
- Thermos Flask: Uses conduction, convection, and radiation prevention to keep liquids hot/cold.
Difference Between Heat and Temperature
| Aspect | Heat | Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Form of energy | Measure of hotness/coldness |
| Unit | Joule (J) | Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F) |
| Measured by | Calorimeter | Thermometer |
| Transfer | Flows from hot to cold object | Indicates thermal state |
Safety Precautions with Heat
- Do not touch hot objects directly.
- Always use protective gloves or tongs.
- Keep inflammable materials away from heat sources.
- Do not overheat thermometers beyond their range.
Summary
- Heat is energy; temperature measures hotness.
- Heat is measured in Joules, temperature in Celsius/Fahrenheit.
- Heat transfer methods: Conduction, Convection, Radiation.
- Black objects absorb heat faster than white objects.
- Clinical thermometer measures human body temperature (37°C normal).
❓ FAQs
Q1. What is the normal human body temperature?
Ans: 37°C (98.6°F).
Q2. Which heat transfer method is used in cooking rice in water?
Ans: Convection.
Q3. Why are cooking utensils made of metals?
Ans: Metals are good conductors of heat.
Q4. Why do we wear light-colored clothes in summer?
Ans: Light colors reflect heat and keep us cool.
Q5. Which method of heat transfer allows sunlight to reach Earth?
Ans: Radiation.

