In Solid State, we shall learn here a about Classification of solids, Unit cells in two and three dimensional lattices, Calculation of density in unit cells, packing in solids, Voids, Number of atoms per unit cell, point defects, electrical and magnetic properties of solids.
What are called solids?
A chemical substance which has definite Volume and definite shape is called solid.
What is Solid State?
A state of a matter in which any substance has definite Volume and definite shape is called Solid State. Example Ice, Brick, Gold, paper, iron etc.
General characteristics of Solid State
A solid has the following properties:
- In a solid, Intermolecular distances are very small.
- Their constituent particles occupy fixed positions and can only oscillate about their mean positions as a result:
- They possess rigidity
- They have high density
- They possess definite shape and definite Volume.
- They are incompressible.
Classification of Solids in Solid State
There are two types of solids based upon the arrangement of constituent particles.
- Crystalline solid
- Amorphous solid
What is Crystalline solid?
That solid in which its constituent particles are arranged in a regular manner consisting of long orders as well as short orders in three dimensional space is called Crystalline solid. Example: All solid elements (metals and non-metals ) and compounds exists in this form.
What is Amorphous solid?
That solid in which its constituent particles are arranged in a irregular manner consisting of short orders only in three dimensional space is called Amorphous solid. Example: rubber, glass, pitch, fused silica, plastics and polymers of high molecular mass.
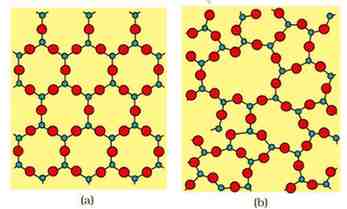
Difference between Crystalline Solid and Amorphous Solid
| Crystalline Solid | Amorphous Solid |
| 1. The constituent particle of this solid are arranged in regular manner in three dimensional space. | 1. The constituent particle of this solid are arranged in irregular manner in three dimensional space. |
| 2. It consists of long orders as well as short orders. | 2. It consists of only short orders. |
| 3. It is anisotropy. | 3. It is isotropy. |
| 4. It has sharp melting point. | 4. It melts at the range of temperature. |
| 5. It gives clear cut cleavage. | 5. It gives irregular cut. |
| 6. It is a true solid | 6. It is pseudo solid or super cooled liquid. |
What is Anisotropy and Isotopy in Solid State?
Anisotropy: This is the behaviour of solid due to which some physical properties like refractive index, thermal conductivity and electrical conductance have different value along all the axis in three dimensional space and this behaviour is known as Anisotropy. This is shown by Crystalline solids.
Isotropy: This is the behaviour of solid due to which some physical properties like refractive index, thermal conductivity and electrical conductance have same value along all the axis in three dimensional space and this behaviour is known as Isotropy. This is shown by Amorphous solids.
Types of Crystalline Solids
Crystalline solids have been further classified into four types. They are followings:
- Ionic solid
- Molecular solid
- Covalent or Network solid
- Metallic solid.
Definition of each type of Crystalline solids in Solid State
- Ionic solid: A crystalline solid which are made of cations and anions and they are linked together by coulombic force is called Ionic solid. Example: NaCl, K2SO4, LiF, MgO, ZnS etc.
- Molecular solid: A crystalline solid in which constituent particles are atom of inert gases or covalent molecules is called Molecular solid. This solid has been further subdivided into three types. They are followings:
- Non-Polar Molecular Solid: In this solid, constituent particles are inert gases or non-polar molecules and they are linked together by dispersion force. Example: H2, Cl2, CH4, CO2, He etc.
- Polar Molecular Solid: In this solid, the constituent particles are polar molecules and they are linked together by dipole-dipole attraction forces. Example: HCl, H2S, SO2 etc.
- Hydrogen Bonded: In this solid, constituent particles contain hydrogen atom linked to F, O or N by hydrogen bond. Example: H2O, NH3, HF, Alcohol etc.
- Covalent or Network solid: A crystalline solid in which the constituent particles are non-metal atoms linked to the adjacent atoms by covalent bonds throughout the crystal is called Covalent or Network solid. Example: SiC, AlN, graphite, diamond, etc.
- Metallic solid: A crystalline solid in which constituent particles are metallic ions in sea of mobile electrons is called Metallic solid. Example: All metals and their alloys.
Important Characteristics of Crystalline Solids
Characteristics of Ionic Solids
- They have high melting and boiling point because of strong electrostatic forces of attraction exist among constituent particles of this solid.
- They are electrical insulator in solid state because their ions are not free to move in solid state. However, in the aqueous solution or in the molten state, they are good conductor of electricity because ions become free in these states.
- They are soluble in polar solvents but insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene or chloroform.
- They are hard but brittle.
Characteristics of Molecular Solids
- Non-polar Molecular Solids: Important characteristics of this solid are followings:
- These solids are generally soft due to presence of weak dispersion forces in them.
- They are bad conductors of electricity due to absence of free ions in them.
- They have low melting and boiling point.
- Due to weak intermolecular forces present in them, they are usually gaseous or liquids at room temperature and pressure.
- Polar molecular solids:
- They are soft.
- They are non-conductor of electricity.
- Their melting and boiling points are comparatively higher than non- polar molecular solids but not so high.
- They exist as gases or liquids at room temperature and ordinary pressure.
- Hydrogen bonded molecular solids:
- They exist as volatile liquids or soft solids at room temperature and ordinary pressure.
- They are non-conductors of electricity.
- Their melting and boiling points are higher than the other two types of molecular solids.
Characteristics of Covalent or Network Solids
- In this solid, covalent bonds are present which are strong and directional hence this solid is very hard and brittle.
- They have extremely high melting points and may even decompose before melting.
- They are insulators and do not conduct electricity. Graphite is an exception because it has free electrons.
Characteristics of Metallic Solids:
- They possess high electrical and thermal conductivity because they have free electrons.
- They possess lustre and colour.
- They are highly malleable and ductile.
- They have high melting points and high densities.
Notes of solution for chemistry 12th chapter two
Electrochemistry for 12th: Notes for chapter 3 of chemistry 12
Chemical Kinetics Class 12: Notes For Chapter 4 Chemical kinetics
FAQS in Solid State
Q.1. Why are Amorphous solids are considered as Supercooled liquids ?
Ans: Like liquids, amorphous solids are isotropic and possess fluidity.
Q.2. How do the structures of quartz and quartz glass differ from each other ?
Ans: Quartz is a Crystalline solid in which constituent particles (SiO4 tetrahedra) are arranged in regular manner while in case of glass its constituent particles (SiO4 tetrahedra) are arranged in regular Pattern and has lack of long range order.
Q.3. Why are solids rigid ?
Ans: The constituent particles in solids have fixed positions and can only oscillate about their mean positions. Hence, they are rigid.
Q.4. Why do solids have a definite Volume ?
Ans: The constituent particles of a solid have fixed positions and are not free to move about.
Q.5. Ionic solids conduct electricity in the molten state but not in the solid state. Why?
Ans: In the molten state, ionic solids dissociate to give free ions and hence can conduct electricity. However, in the solid state, their ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction and not free to move.
